Serpentine 6.2 Liter Ford 6.2 Belt Diagram: Routing Guide
The serpentine 6.2 liter Ford 6.2 belt diagram illustrates the belt path around the crankshaft, alternator, water pump, and A/C compressor. To install, use a breaker bar to rotate the spring-loaded tensioner, route the belt according to the visual guide, and ensure the ribs are fully seated in the pulley grooves.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Visualizes the correct path to prevent engine overheating or charging failure
- Identify the automatic tensioner as the primary adjustment point
- Always disconnect the battery to prevent accidental engine starts
- Check all pulleys for play or noise before installing a new belt
- Use this diagram whenever the belt is removed for alternator or pump service
Finding yourself under the hood of a Ford Super Duty or F-150 equipped with the powerhouse 6.2L V8 engine often leads to one specific challenge: navigating the complex web of the accessory drive system. Whether you are performing routine maintenance or responding to an emergency roadside failure, having access to a clear and accurate serpentine 6.2 liter ford 6.2 belt diagram is the difference between a successful repair and a frustrating afternoon. This comprehensive guide is designed to deconstruct the routing path of your belt, identify every pulley involved in the system, and provide the technical specifications required to ensure your engine remains in peak operating condition. By the end of this article, you will understand not just how the belt sits on the engine, but how it interacts with vital systems like the alternator, water pump, and power steering pump.
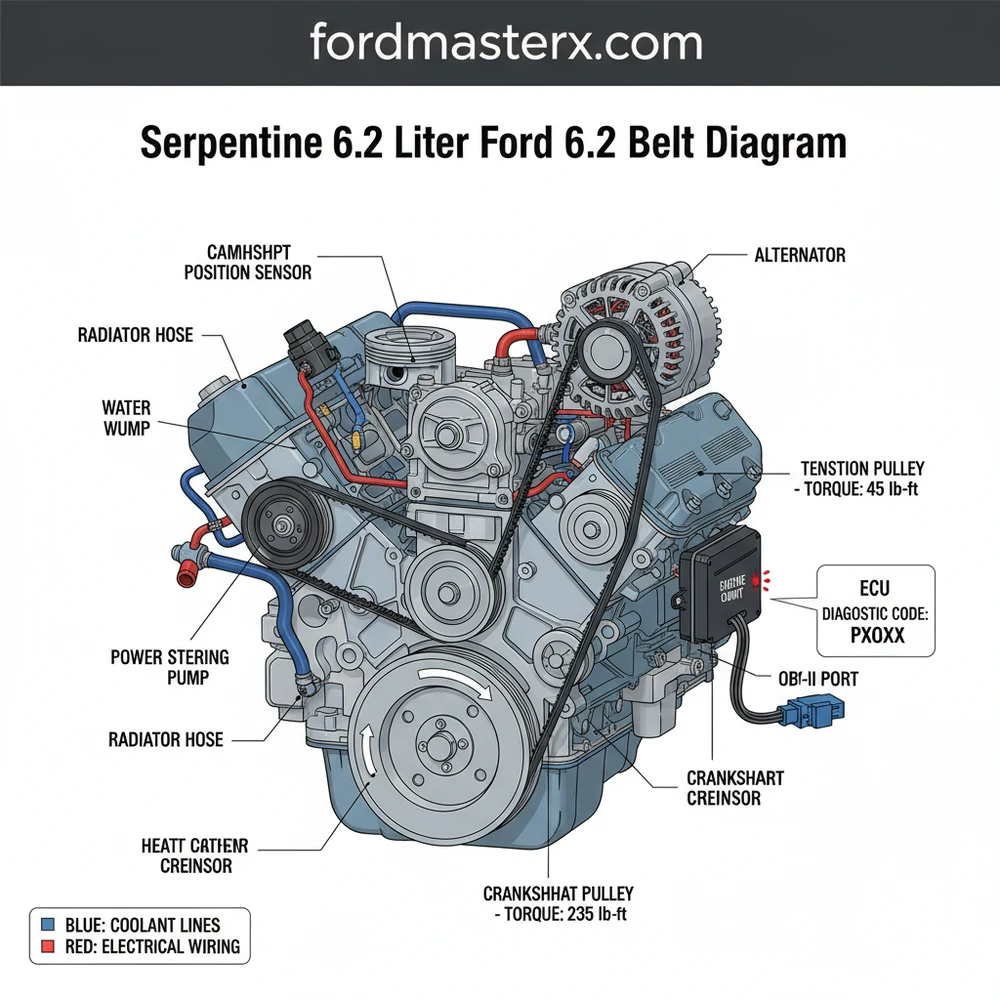
Understanding the 6.2L Accessory Drive Layout
The Ford 6.2L engine, often referred to as the “Boss” V8, utilizes a single, long serpentine belt to drive all external components. This system is known as an accessory belt drive, and its efficiency is paramount to the vehicle’s operation. Unlike the internal timing chain, which is protected within the engine block and lubricated by oil, the serpentine belt is exposed to heat, debris, and friction. The diagram for this engine highlights a “wrap-around” design that ensures maximum surface contact between the belt and the pulleys to prevent slippage under heavy loads.
In a standard configuration, the serpentine 6.2 liter ford 6.2 belt diagram identifies several key components. At the very bottom center is the crankshaft pulley, which provides the rotational force for the entire system. From there, the belt travels upward to the water pump, which is critical for maintaining consistent coolant flow throughout the engine block and radiator. The belt then snakes around the alternator, the power steering pump (on models not equipped with electric power steering), and the air conditioning compressor. To keep everything tight, the system employs an automatic tensioner pulley and one or more idler pulleys, which serve to redirect the belt and maintain the necessary tension.
(Visual representation: The belt starts at the Crankshaft (bottom), goes up to the Water Pump, loops over the Alternator (top right), down to the Idler Pulley, around the AC Compressor (bottom right), across to the Tensioner, and over the Power Steering Pump (left) before returning to the Crankshaft.)
On the 6.2L Ford engine, the belt routing can vary slightly depending on whether the vehicle has a dual-alternator setup or specific heavy-duty cooling packages. Always verify if your truck has secondary accessories before removing the primary belt.
Step-by-Step Installation and Routing Guide

Interpreting the serpentine 6.2 liter ford 6.2 belt diagram is the first step, but physical installation requires a methodical approach. Before you begin, ensure the engine is completely cool to the touch. Working around a hot radiator or exhaust manifold can lead to serious injury.
- ✓ Step 1: Preparation and Tool Selection. You will need a 1/2-inch drive breaker bar or a dedicated serpentine belt tool. Most 6.2L tensioners feature a square female insert or a specific bolt head (usually 15mm) that allows you to rotate the tensioner arm.
- ✓ Step 2: Relieving Tension. Insert your tool into the tensioner. Rotate the tensioner clockwise (toward the passenger side) to compress the internal spring. This will create slack in the belt, allowing you to slip it off the topmost idler pulley.
- ✓ Step 3: Removing the Old Belt. Carefully feed the belt out from around the fan blade (if equipped with a mechanical fan) and away from the pulleys. This is a good time to inspect each pulley by hand; they should spin freely without any grinding noise or side-to-side play.
- ✓ Step 4: Initial Routing. Following your diagram, begin at the crankshaft at the bottom. Route the belt upward, ensuring the “ribbed” side of the belt matches the “grooved” pulleys and the “smooth” side matches the “smooth” idler pulleys.
- ✓ Step 5: The Final Loop. Save the easiest pulley for last—usually a smooth idler or the alternator. While holding the tensioner in the compressed position with one hand, slide the belt onto the final pulley with the other.
- ✓ Step 6: Verification. Release the tensioner slowly. Double-check that the belt is perfectly centered in every groove. If the belt is even one rib off, it will shred within minutes of starting the engine.
Never place your fingers between the belt and the pulley while the tensioner is compressed. If the tool slips, the tensioner can snap back with enough force to cause severe injury or bone fractures.
When performing this task, pay close attention to the torque spec of the tensioner mounting bolt if you are replacing the entire assembly. For the Ford 6.2L, the tensioner assembly bolt typically requires a torque of approximately 35-40 lb-ft, though you should always consult your specific service manual to account for year-to-year updates.
Common Issues and Diagnostic Troubleshooting

The serpentine belt is a window into the health of your engine’s electrical and cooling systems. If the belt fails, the alternator stops charging, which the ECU (Engine Control Unit) will immediately detect. This typically results in a battery warning light on the dashboard and may trigger a check engine light. Using an OBD-II scanner, you might find a diagnostic code related to low system voltage (such as P0562).
Another critical failure point involves the water pump. Since the belt facilitates coolant flow, a snapped belt will cause the engine temperature to spike almost instantly. If you notice the temperature gauge rising rapidly, pull over immediately. The serpentine 6.2 liter ford 6.2 belt diagram serves as a troubleshooting map; for instance, if you hear a high-pitched squeal that changes with engine RPM, you can use the diagram to identify which pulley might be seizing. A seized A/C compressor or alternator can create enough friction to burn through a brand-new belt in seconds.
Use a spray bottle with plain water to test for belt noise. If a light mist of water silences the squeal, the belt is likely glazed or misaligned. If the noise gets louder or stays the same, you likely have a failing pulley bearing.
Best Practices and Maintenance Tips
To maximize the lifespan of your accessory belt, routine inspection is mandatory. Ford recommends inspecting the belt every 30,000 miles, though modern EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) belts do not crack as easily as older neoprene belts. Instead, they lose material in the grooves—much like a tire loses tread. You can use a belt wear gauge to check if the grooves have become too deep, which prevents the belt from gripping the pulleys correctly.
When it comes to replacement, always choose a high-quality, name-brand belt. While budget options are available, the 6.2L engine is often used in heavy-duty towing applications where high heat and high RPMs are common. A premium belt with aramid fiber reinforcement will offer better resistance to stretching and heat. Furthermore, consider replacing the tensioner and idler pulleys at the same time as the belt. These components have bearings that wear out at similar intervals; putting a brand-new, tight belt on an old, worn tensioner often leads to premature failure of the new part.
Regarding long-term engine health, remember that while the serpentine belt is a 100,000-mile service item for many, the internal timing chain is designed to last the life of the engine. However, a failure in the accessory drive (like a seized water pump) can lead to overheating that compromises the entire engine’s structural integrity. Maintaining the belt according to the serpentine 6.2 liter ford 6.2 belt diagram is a small investment that protects the much more expensive internal components of your Ford V8.
In conclusion, maintaining the accessory drive system on your 6.2L Ford is an essential skill for any owner. By understanding the routing diagram, utilizing the correct tools, and keeping an eye on diagnostic cues from the ECU and OBD-II system, you ensure that your truck remains reliable whether you are on a job site or a cross-country haul. Proper belt tension and alignment are the silent guardians of your engine’s performance—treat them with the attention they deserve.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is the belt tensioner located?
On the Ford 6.2L engine, the serpentine belt tensioner is typically located on the front of the engine block, situated between the alternator and the crankshaft pulley. It features a spring-loaded arm with a pulley that maintains constant pressure on the belt to prevent slipping during operation.
What does the serpentine belt diagram show?
This diagram provides a clear visual map of how the belt wraps around various engine accessories. It identifies the crankshaft (power source), alternator, water pump, power steering pump, and A/C compressor, ensuring the belt is routed with the correct side facing each pulley for maximum grip.
How many pulleys are on the 6.2L Ford engine?
The Ford 6.2L V8 engine generally utilizes a seven or eight-pulley system. This includes the crankshaft balancer, alternator, water pump, A/C compressor, power steering pump, the automatic tensioner pulley, and one or more idler pulleys designed to guide the belt across long spans of the engine front.
What are the symptoms of a bad serpentine belt?
Common symptoms include loud squealing noises, visible cracks or fraying, and loss of power steering. If the belt slips significantly, the ECU may trigger a check engine light or battery warning. You can use an OBD-II scanner to check for a diagnostic code related to charging system voltage.
Can I replace the 6.2L serpentine belt myself?
Yes, replacing the belt on a Ford 6.2L engine is a straightforward DIY task. It requires basic hand tools and about 30 minutes of time. Having the serpentine 6.2 liter Ford 6.2 belt diagram handy is essential to ensure the new belt is routed correctly and safely.
What tools do I need for this belt replacement?
You will primarily need a 1/2-inch drive breaker bar or a dedicated serpentine belt tool to rotate the tensioner. A flashlight is helpful for inspecting the lower pulleys, and a torque wrench is recommended if you are replacing the tensioner assembly to meet the manufacturer’s torque spec.






