The Definitive Engineering and Operational Report on Ford Connectivity: Architecture, Configuration, and Diagnostics of In-Vehicle Wi-Fi Systems
The modern automotive landscape has shifted fundamentally from mechanical isolation to hyper-connectivity. The Ford vehicle of the post-2016 era is no longer merely a means of transportation; it is a sophisticated node within the Internet of Things (IoT), functioning simultaneously as a client, a server, and a telemetry broadcast station. For the owner, fleet manager, or technician, the phrase “connecting to Ford Wi-Fi” is often ambiguous,
referring to two distinct yet interrelated technical operations: Inbound Connectivity, where the vehicle connects to a stationary Wide Area Network (WAN) for firmware maintenance, and Outbound Connectivity, where the vehicle utilizes its embedded cellular modem to broadcast a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) for passenger use.
This report serves as an exhaustive technical dossier on the Ford connectivity stack. It dissects the interaction between the Accessory Protocol Interface Module (APIM) and the Telematics Control Unit (TCU), details the configuration protocols for SYNC 3, SYNC 4, and SYNC 4A architectures, and provides a deep-dive diagnostic framework for resolving common failures such as “greyed out” connectivity controls, authentication loops, and data provisioning errors.
By synthesizing data from official Ford technical documents, user feedback loops, and cellular carrier specifications, this analysis aims to be the singular reference point for understanding the digital nervous system of Ford vehicles.
How to Connect to Ford Wi-Fi
Turn your vehicle into a powerful 4G LTE hotspot. A complete data-driven guide to activating FordPass Connect, maximizing speed, and managing your AT&T data trial.
The Connection Protocol
Activating your Ford’s hotspot is a straightforward 4-step process. Follow this workflow to get up to 10 devices online instantly.
Access Settings
Start your vehicle. On the SYNC 3 or SYNC 4 touchscreen, tap Settings and swipe to select Wi-Fi & Hotspot.
View Credentials
Tap “Vehicle Hotspot”. Ensure the toggle is ON. Tap “View Password” to reveal the SSID and default key.
Connect Device
On your phone or tablet, search for Wi-Fi networks. Select your Ford’s network name and enter the password displayed on the screen.
Activate Trial
Once connected, a browser portal should open. If not, navigate to the AT&T portal to activate your 3-Month/3GB free trial.
Performance Analysis
*Ratings based on standard 4G LTE automotive antenna gain vs. average smartphone internals.
Why Use the Built-in Hotspot?
Superior Signal Gain
Your Ford utilizes a powerful external shark-fin antenna, providing a stronger, more consistent signal in rural areas compared to a smartphone inside the metal cabin.
Battery Conservation
Tethering drains your smartphone battery rapidly. Using the vehicle’s hotspot saves your phone’s power for when you reach your destination.
© 2026 FordMasterX Infographics. Data sourced from manufacturer owner manuals.
Understanding the 3GB Trial
New Ford vehicles come with a complimentary trial of 3 Months or 3GB of data (whichever comes first). But what does 3GB actually look like in real-world usage?
Tips to conserve data:
- Download maps offline via SYNC updates.
- Set video streaming quality to 480p (Standard Definition).
- Disable “Auto-Play” on social media apps for passengers.
External Resource
Manage your plan directly at the AT&T Vehicle Portal .
Potential 3GB Consumption Breakdown
*Estimates based on standard bitrate consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Hardware Ecosystem: The Digital Nervous System

To truly master the connectivity settings of a Ford vehicle, one must first understand the underlying hardware architecture that facilitates these signals. The connectivity stack is not a monolithic entity but a synchronized dance between two primary modules, communicating over the vehicle's Controller Area Network (CAN) bus.
The Accessory Protocol Interface Module (APIM)
The APIM is the central processing unit of the infotainment experience. Located physically behind the capacitive touch screen (or the non-touch display in base models), the APIM is responsible for the Human-Machine Interface (HMI). It runs the operating system—QNX in SYNC 3 and a more advanced, cloud-native iteration in SYNC 4.
- Role in Connectivity: The APIM houses the Wi-Fi radio used for Inbound connections. When you connect your F-150 or Explorer to your home router to download a map update, the APIM is the active client.
- Evolution: The shift from SYNC 3 to SYNC 4 represented a doubling of computing power.2 While SYNC 3’s APIM focused on localized processing, the SYNC 4 APIM is designed for "always-on" cloud integration, constantly pinging remote servers for navigation traffic data and natural voice processing.
The Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
While the APIM manages the screen, the TCU is the gateway to the outside world while the vehicle is in motion. This module contains the 4G LTE modem (and in future iterations, 5G).
- Role in Connectivity: The TCU manages the Outbound hotspot. It authenticates with the cellular carrier (AT&T in North America) via an embedded SIM (eSIM) and broadcasts the signal to the vehicle's internal antenna array.4
- The Critical Link: Many user frustrations, such as the "greyed out" Wi-Fi button, stem from a failure in the heartbeat signal between the APIM and the TCU. If the APIM cannot verify the TCU's status via the CAN bus, it disables the UI controls to prevent user error, leading to the dreaded "greyed out" symptom.5
The Antenna Array and Signal Propagation
Unlike a smartphone, which is subject to the shielding effects of the vehicle's steel, aluminum, or boron chassis, the Ford connectivity system utilizes a "shark fin" or roof-mounted antenna assembly. This provides a significantly higher gain, allowing the TCU to maintain a cellular handshake in fringe coverage areas where a mobile phone might drop to 3G or lose signal entirely.4 This architectural advantage is the primary value proposition of the in-vehicle hotspot for rural travelers and contractors.
Inbound Connectivity: Connecting the Vehicle to External Wi-Fi

For the majority of Ford owners, the primary motivation to connect the vehicle itself to a Wi-Fi network is to facilitate software updates without the inconvenience of visiting a dealership. This "Client Mode" operation is critical for maintaining the health of the APIM software, patching Bluetooth interoperability bugs, and updating navigation cartography.
The Strategic Necessity of Wi-Fi Updates
In the era of Software Defined Vehicles (SDVs), the code controlling the infotainment system is dynamic. Ford releases periodic updates to address compatibility with new iOS or Android versions, fix latency issues, and patch security vulnerabilities.
- Data Volume: A typical SYNC 3 navigation update can exceed 15GB of data. While cellular networks are capable of handling this, the cost of data transmission is prohibitive for the manufacturer. Therefore, Ford engineers designed the system to offload these massive payloads to the owner's unmetered home Wi-Fi connection.3
- The "Check-In" Logic: The system does not maintain a constant connection. Instead, it wakes up periodically or utilizes "Power-Up" schedules to scan for differential update packages, downloading only the altered code to minimize bandwidth usage.
SYNC 3 Connectivity Architecture
SYNC 3, introduced roughly around 2016, represented a major stabilization of Ford’s infotainment strategy after the turbulent MyFord Touch era. It supports Wi-Fi updates, but unlike its successor, it is not "always connected" to the cloud for deep navigational data without a paired phone.
Configuration Protocol for SYNC 3 (Touchscreen)
The process of connecting a SYNC 3 unit to a home network is straightforward but intolerant of weak signals.
- Initiate Settings: From the Home screen, tap the Settings icon in the bottom feature bar.6
- Access Network Menu: Swipe to find and select Wi-Fi & Hotspot. In earlier software builds (v3.0 or lower), this may simply be labeled Wi-Fi.
- Enable Radio: Ensure the System Wi-Fi toggle is set to On. You may hear a momentary pause in audio as the radio initializes.
- Network Selection: Tap View Available Networks. The system will scan for 2.4GHz and 5GHz broadcasts.
- Authentication: Select the target network. A keyboard will appear for password entry.
- Verification: Once connected, the network name will appear with a signal strength indicator.
Technical Constraint - The "WPA3" Barrier: SYNC 3 hardware was finalized before the widespread adoption of WPA3 security protocols. Users with modern mesh network routers (e.g., Eero Pro 6, Google Nest Wifi) configured to WPA3-Only mode may find their Ford vehicle refuses to connect or repeatedly drops the connection.
- Remediation: It is highly recommended to enable a "Guest Network" on the home router using the legacy WPA2 Personal protocol specifically for IoT devices like the vehicle.7
Configuration Protocol for SYNC 3 (Non-Touchscreen)
It is a common misconception that all SYNC 3 systems have touch capability. Certain base model F-150s and Transits from 2016-2017 feature a 4.2-inch non-touch color screen controlled by buttons.
- Update Limitation: Crucially, many of these non-touchscreen units do not support Wi-Fi updates.3 The hardware lacks the necessary Wi-Fi radio module.
- Alternative Method: For these units, the only viable update path is the "Sneaker-Net" method: downloading the files to a USB drive (formatted to ExFAT) via the Ford Support website and physically inserting it into the vehicle’s media hub.
SYNC 4 and 4A Connectivity Architecture

SYNC 4 (standard landscape orientation) and SYNC 4A (vertical portrait orientation, found in the Mustang Mach-E and Edge) utilize a cloud-native connectivity stack. This system is designed for seamless "Ford Power-Up" OTA updates, which can download in the background while the vehicle is running or scheduled during the night.
Configuration Protocol for SYNC 4/4A
The menu structure for SYNC 4 has been streamlined, often burying connectivity settings deeper within the "Vehicle" sub-menus compared to SYNC 3.
- Access Menu: Tap the Vehicle image or the Settings gear icon (varies by screen layout/firmware version).
- Connectivity Sub-System: Select Connectivity. This menu aggregates all radio functions (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Telematics).
- Network Management: Press Manage Wi-Fi Networks.
- Enable & Connect: Toggle System Wi-Fi to On and select View Available Networks.
- Connection: Select the SSID and enter the credentials.
Table 1: Technical Comparison of SYNC 3 vs. SYNC 4 Connectivity
| Feature | SYNC 3 Architecture | SYNC 4 / 4A Architecture |
| Primary Connection | Wired (USB) / Bluetooth | Wireless (Cloud Native) |
| Update Method | Wi-Fi (Manual Trigger) or USB | Wi-Fi & Cellular (Automatic OTA) |
| Navigation Data | Static Maps (Stored on Internal Flash) | Cloud-Based (Streaming Real-Time) |
| Smartphone Projection | Wired Android Auto / Apple CarPlay | Wireless Android Auto / Apple CarPlay |
| Screen Sizes | 6.5" or 8" | 8", 12", or 15.5" |
| Processor Power | Baseline | 2x Compute Power of SYNC 3 |
| Wi-Fi Protocol | WPA2 Personal | WPA2 / WPA3 (Hardware Dependent) |
Data synthesized from.2
The Captive Portal Challenge (Eduroam, Hotels, & Airports)
A persistent frustration for owners living in apartments, dormitories, or staying in hotels is the inability to connect their vehicle to "public" Wi-Fi networks that use a Captive Portal.
- The Mechanism: A captive portal intercepts the first HTTP request and redirects the user to a login page (to accept terms, enter a room number, or log in with a student ID).
- The Failure: The browser implementation in SYNC (even SYNC 4) is restricted for safety and security reasons. It often lacks the ability to pop up this redirect page, causing the connection to hang at "Connecting..." indefinitely.
- Case Study: Eduroam: University networks like Eduroam use 802.1x enterprise authentication, which requires installing certificates. The SYNC system generally does not expose a file system to the user to install these certificates.
Workarounds for Captive Portals
Since the vehicle cannot navigate the web page, the network must be tricked into accepting the vehicle.
- MAC Address Whitelisting: Every network interface has a unique Media Access Control (MAC) address.
- Action: Navigate to Settings > General > About SYNC to find the Wi-Fi MAC Address.
- Execution: Provide this alphanumeric string to the network administrator (IT department) to manually whitelist the device, bypassing the portal.
- The Travel Router Solution: A robust solution for road warriors is to use a portable travel router (e.g., TP-Link or GL.iNet).
- Execution: The travel router connects to the hotel/university Wi-Fi (handling the captive portal via a smartphone app) and then rebroadcasts a standard, private WPA2 network (e.g., "FordUpdateNet") that the vehicle can connect to easily.
Outbound Connectivity: The 4G LTE Wi-Fi Hotspot
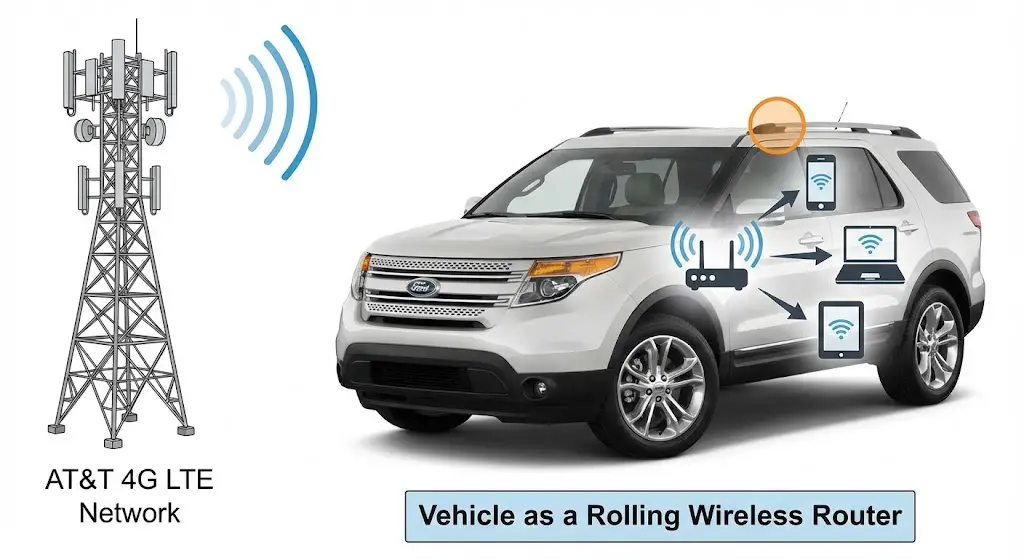
While inbound connectivity updates the car, Outbound Connectivity updates the passengers. This feature, branded as FordPass Connect, transforms the vehicle into a rolling 4G LTE wireless router, supporting up to 10 simultaneous devices.
Carrier Architecture and Market Exclusivity
The telematics hardware in modern Ford vehicles (2018+ and select 2017s) is engineered with a deep integration with AT&T in the North American market.
- Hardware Lock: The TCU contains an eSIM (embedded SIM) or a physically locked SIM tray provisioned specifically for the AT&T network architecture.
- The "Verizon Question": Owners frequently inquire if they can switch the provider to Verizon or T-Mobile to match their personal family plans. The answer is technically no.10 The modem firmware and frequency band support are optimized for AT&T. While some advanced hardware hackers might attempt to swap the TCU, there is no officially supported method to carrier-unlock a Ford vehicle.
- Implication: Regardless of who provides your phone service, your car is an AT&T subscriber. This operates similarly to an iPad with a cellular plan; it is an independent line of service.
Pricing and Economics
As of the 2025/2026 market landscape, the pricing structure for in-vehicle data has stabilized around prepaid models.
- The Trial: New vehicles typically come with a complimentary trial. This is usually 3 Months or 3GB of data, whichever occurs first.4 Critical Warning: The clock on the 3-month trial starts ticking upon the vehicle sale date or the first time the modem is activated at the dealership. It does not pause if the owner leaves the car in the garage for two months.
- Subscription Costs: Once the trial expires, a paid subscription is required.
- Existing AT&T Clients: Can often add the vehicle to their "Unlimited Elite" or "Premium" family plans for approximately $20 per month.
- Non-AT&T Clients: Must set up a standalone prepaid account via the AT&T Connected Car portal. Pricing for unlimited data typically hovers around $25 per month.
Activation Protocol: A Multi-Stage Handshake
Activating the hotspot is not as simple as flipping a switch. It requires synchronizing the vehicle hardware, the Ford cloud, and the AT&T billing system.
Step 1: Vehicle and App Pairing
Before the Wi-Fi can be broadcast, the modem must be authorized to ensure that a neighbor cannot hijack your car's data plan.
- Download & Account: Install the FordPass App (iOS or Android) and create a Ford Owner account.
- Add Vehicle: Tap "Add Vehicle" and scan the VIN barcode located on the driver’s door jamb. Alternatively, manually type the VIN found on the lower driver-side dashboard.15
- Resource: For guidance on deciphering VIN specifics.
- Authorization: Start the vehicle. A prompt will appear on the SYNC touchscreen asking to "Allow" the remote connection. You must physically be in the car to confirm this, binding the phone to the TCU.
Step 2: Enabling the Hotspot Broadcast
- SYNC 4 Setup: Navigate to Settings > Connectivity > Vehicle Hotspot.
- Toggle On: Slide the Vehicle Hotspot switch to On.
- Network Configuration: To view the SSID (Network Name) and default password, select Settings > Edit within the hotspot menu.
- Security Recommendation: The factory password is secure but hard to remember. It is highly recommended to change the SSID to something recognizable (e.g., "Bronco_Adventure_Net") and set a strong WPA2 password.
Step 3: Data Plan Provisioning
Turning the hotspot "On" creates a Local Area Network (LAN), but without a data plan, it has no Wide Area Network (WAN) uplink.
- Initiate Setup: Open the FordPass App, navigate to the Vehicle Hotspot tile, and select Manage my account.
- Portal Redirect: This will launch a browser window redirecting to the AT&T Connected Car portal.
- Account Creation: Create an AT&T account (separate from your personal cellular account if you are not an AT&T customer) and input credit card details for the subscription post-trial.
The WarnerMedia RIDE Experiment
For a period (circa 2020-2023), Ford and AT&T aggressively marketed a bundle called WarnerMedia RIDE. This service allowed devices connected to the vehicle Wi-Fi to stream content from HBO, Cartoon Network, and CNN without counting against data caps (if caps existed) or as a value-add.
- Current Status: As of 2025, the streaming landscape has fragmented. WarnerMedia has undergone mergers (Discovery), and carrier value-added services are often restructured. Users should verify the current availability of this specific bundle in the AT&T portal, as reports indicate it may have been discontinued or rolled into standard "Unlimited" offerings without the specific branding.
The FordPass Ecosystem and Cloud Handshakes
Connectivity is the backbone of the FordPass ecosystem. It is not merely about Wi-Fi; it is about remote command and control. The FordPass App communicates with the vehicle via the cloud, which then relays commands to the TCU.
Features Dependent on Connectivity
- Remote Start/Stop: The ability to start the engine from miles away relies entirely on the TCU having a cellular signal.
- Lock/Unlock: Vital for users who lock their keys in the car.
- Vehicle Location: GPS data is transmitted via the modem to the app.
- SecuriAlert: If a door is opened while the vehicle is parked, the TCU pushes a notification to the phone.
- FordPass Rewards: Earning points for service visits and vehicle purchases is tied to the connected account. For a detailed breakdown of the rewards architecture.
The "Activation Pending" Loop: A Deep Dive
One of the most pervasive issues owners face is the "Activation Pending" status in the FordPass App that never resolves.20
- The Technical Failure: This occurs when the cryptographic token exchange between the Ford Cloud, the App, and the Vehicle Module (TCU) becomes desynchronized. The app thinks it is waiting for the car; the car thinks it is already connected (or has denied the connection).
- Resolution Protocol:
- Toggle Connectivity: In the vehicle, go to Settings > Connectivity > Connected Vehicle Features. Toggle Vehicle Connectivity to OFF.
- Wait: Allow the system to sit for 60 seconds to terminate the session.
- Toggle On: Switch Vehicle Connectivity back to ON.
- App Refresh: Close and reopen the FordPass App. If the prompt does not appear, you may need to Delete the Vehicle from the app entirely and re-scan the VIN to force a fresh handshake.
Deep Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
The most complex aspect of Ford Wi-Fi is diagnosing failures. When the system works, it is invisible. When it fails, it is a source of immense frustration. Failures generally manifest in three ways: the "Greyed Out" interface, the "Connected but No Internet" state, and physical hardware absence.
The "Greyed Out" Wi-Fi Button

Symptom: The user navigates to the Settings menu, but the "Wi-Fi" or "Vehicle Hotspot" button is greyed out (disabled) and unresponsive to touch.
Root Cause: This is a Communication Failure. The APIM (Screen) cannot see the TCU (Modem). This can happen if the modem is in a "deep sleep" state to preserve battery, if the software driver has hung, or if the hardware has failed.
Remediation Level 1: The "Key Cycle"
Computers in cars do not turn off immediately when you remove the key. They enter a standby mode. To force a true reboot:
- Turn the vehicle off.
- Open the driver's door (this triggers the "Retained Accessory Power" kill signal).
- Close the door and lock the vehicle.
- Wait 35 minutes. This duration is critical as it is the standard timeout for modules to enter "Sleep" mode.
- Restart the vehicle and check connectivity.
Remediation Level 2: The Master Reset
A Master Reset clears user data and forces a complete software reload of the APIM.
- SYNC 3: Settings > General > Master Reset.
- SYNC 4: Settings > General > Reset > Factory Reset.
- Digital Experience: Settings > System > Reset options > Factory reset.
- Warning: This is a destructive process. It will delete paired phones, navigation favourites, and stored Wi-Fi networks.
Remediation Level 3: The Hard Module Reset (Fuse Pull)
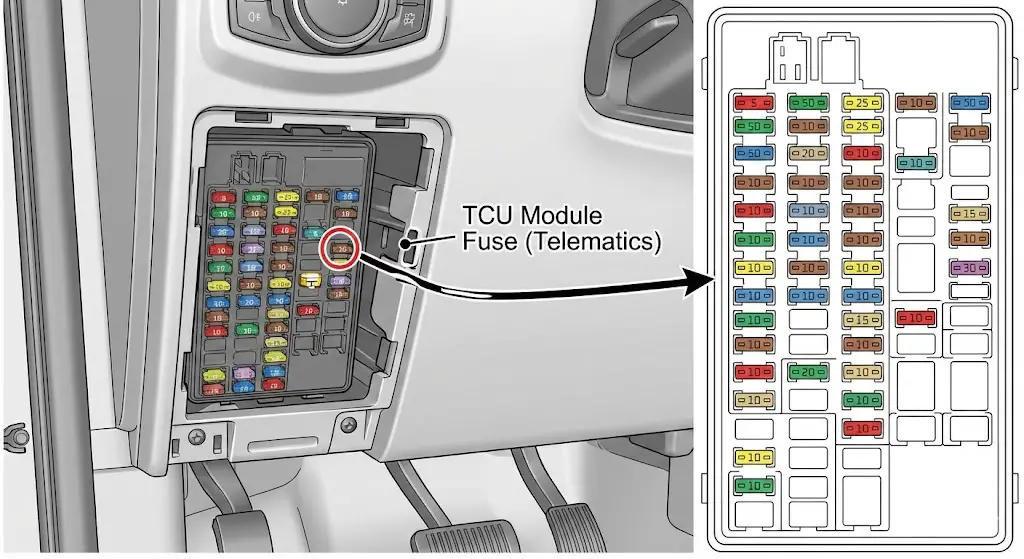
If software resets fail, the hardware needs a power cut.
- The Battery Method: Disconnect the negative battery terminal for 10-15 minutes. Note: This resets all modules, including the PCM and TCM, and may trigger anti-theft protocols.
- The Fuse Method: A more surgical approach is to pull the specific fuse for the TCU.
- F-150 / Bronco: Often Fuse 32 or Fuse 20 in the passenger footwell (Body Control Module).
- Procedure: Remove the fuse, wait 5 minutes for the capacitors to discharge, and reinstall. This forces the modem to re-register with the cellular tower.
"Connected But No Internet"
Symptom: Client devices connect to the vehicle's Wi-Fi SSID with strong signal, but cannot load webpages.
Root Cause:
- Data Plan Expiry: The most common cause is a lapsed AT&T subscription or exhausted data cap. The LAN is working (you are talking to the car), but the WAN is blocked (the car is not talking to the internet).
- DNS Conflict: The device may not be receiving a valid IP address or DNS server from the car's DHCP server.Remediation:
- Check Plan: Verify the Data Plan status in the FordPass App or AT&T portal.
- Network Reset: "Forget" the network on the client device (iPhone/Android) and reconnect. This forces a flush of the IP and DNS settings.
Model-Specific Nuances and The Chip Shortage
Not all Ford vehicles are created equal regarding connectivity. The global semiconductor shortage (2021-2023) introduced significant variances in build configurations.
The "Hotspot Removal" Option

During the height of the supply chain crisis, Ford (and other manufacturers) faced a shortage of telematics chips. To keep assembly lines moving, thousands of vehicles—particularly the Bronco, Maverick, and Escape—were built with the "4G LTE Wi-Fi Hotspot Removal" option.
- Identification: Users must check the original window sticker (Monroney Label). Look for a line item under "Optional Equipment" that reads "4G LTE Wi-Fi Hotspot Removal" accompanied by a small credit (usually -$20.00).
- The Reality: If this credit exists on the sticker, the vehicle physically lacks the hardware functionality for the hotspot. No software update, Forscan hack, or dealer service can enable it. The modem may still exist for basic low-bandwidth telematics (remote lock/unlock), but the high-bandwidth Wi-Fi broadcast capability is hardware-deleted.
- Buying Advice: Used car buyers looking for a mobile office should verify the window sticker or run a VIN decode before purchase. Refer to the(https://fordmasterx.com/ford-suv-size-chart/) for general model specs, but always verify the specific VIN for connectivity features.
EV Specifics: Mustang Mach-E and F-150 Lightning
For electric vehicles, connectivity is operational critical.
- Charging Logistics: The vehicle communicates with the Ford Cloud to manage charging schedules, preventing charging during peak rate hours.
- Pre-Conditioning: Users often "start" the car remotely to warm the battery and cabin while still plugged in, preserving range. This requires a stable TCU connection.
- Power-Up Updates: EVs receive more frequent updates to optimize thermal management and range algorithms. Ensuring the vehicle is connected to home Wi-Fi is crucial, as these updates are often too large for the cellular connection.
Future Outlook: 5G and V2X
The capability to connect to Ford Wi-Fi—whether for downloading the latest SYNC software or powering a mobile office—is a fundamental aspect of the modern ownership experience.
The Shift to 5G
Current vehicles (up to roughly 2024) rely primarily on 4G LTE modems. The next generation of the Ford Digital Experience (android-based infotainment appearing in 2025 models) will transition to 5G modems.
- Benefit: Lower latency and higher throughput will enable cloud-based gaming, higher-definition video streaming, and faster OTA updates.
- V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything): 5G is the enabler for V2X, where the vehicle communicates with traffic lights, other cars, and infrastructure to improve safety and traffic flow.
Maintenance as a Mindset
Technicians and owners must now treat connectivity issues with the same rigor as mechanical failures. A "greyed out" Wi-Fi button is the "Check Engine Light" of the digital cabin. Troubleshooting requires a systematic approach—from soft resets to fuse pulls—before condemning expensive hardware. Furthermore, as vehicles become more integrated with other systems, understanding the ripple effects is key. For example, a failure in the instrument cluster can disrupt the network bus, affecting connectivity; for more on cluster diagnostics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I switch my Ford Wi-Fi hotspot from AT&T to Verizon or T-Mobile?
A: No. The internal modem (TCU) uses an eSIM or hardware configuration locked to AT&T's network bands and provisioning system. To use a different carrier, you must use an external mobile hotspot device or your smartphone.
Q: How much does the Ford Wi-Fi hotspot cost?
A: After the complimentary trial (usually 3 months or 3GB), plans typically start around $20/month for unlimited data for existing AT&T customers, or $25/month for standalone prepaid plans. Prices are subject to change by AT&T.
Q: Why is my "Vehicle Hotspot" button greyed out?
A: This indicates the SYNC system cannot communicate with the modem. Try performing a Master Reset or a "key cycle" (turn off the car, open the door, wait 35 minutes). If it persists, it may be a blown fuse (Fuse 32/20) or a failed TCU.
Q: Can I update my SYNC 3 system without Wi-Fi?
A: Yes. You can download the update file from the Ford Support website to a USB drive (formatted to ExFAT) and plug it into the vehicle's USB port to perform the update manually.
Q: How do I find my Ford Wi-Fi password?
A: On SYNC 3, go to Settings > Wi-Fi & Hotspot > View Password. On SYNC 4, go to Settings > Connectivity > Vehicle Hotspot > Settings > Edit to view or change the password.
Q: My FordPass app says "Activation Pending" forever. How do I fix it?
A: This is a common synchronization error. Go to your vehicle's Connectivity Settings, toggle "Vehicle Connectivity" OFF and then ON again. Then, delete the vehicle from the FordPass app and re-add it by scanning the VIN again.
Q: Does the Wi-Fi hotspot work when the car is off?
A: Generally, no. The vehicle must be in "Accessory" mode or the engine must be running to power the modem and broadcast the signal. Using it in Accessory mode for extended periods will drain the 12V battery.







