6.0 Powerstroke Hp And Torque: Factory Specifications And Performance Upgrades
The 6.0L Powerstroke diesel engine remains a legendary yet misunderstood powerhouse in the Ford Super Duty lineup, famous for its distinctive VGT whistle and impressive high-RPM performance. While factory ratings were competitive for the era, many owners find themselves confused by how to accurately measure stock output versus the potential gains of aftermarket modifications without compromising engine longevity. This article provides a professional analysis of the 6.0 Powerstroke hp and torque specifications, exploring both factory engineering and the expert-recommended upgrades required to reach 500+ horsepower reliably. Whether you are maintaining a daily driver or building a dedicated tow rig, understanding the mechanical baseline of this platform is the first step toward achieving a high-quality, high-performance build.
Standard 6.0 Powerstroke HP and Torque Ratings Across Model Years

📤 Share Image
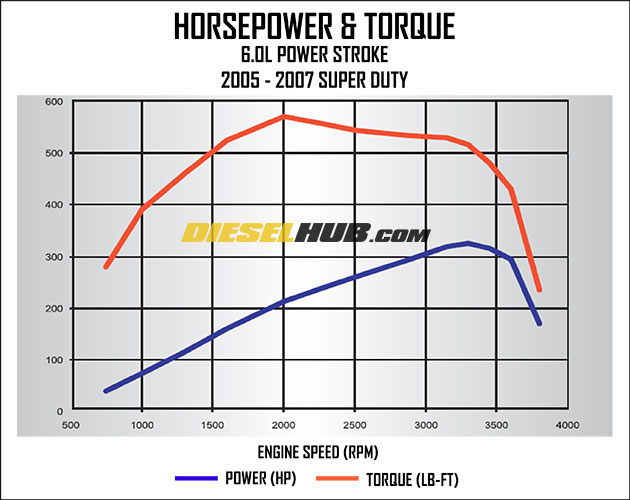
To understand the performance potential of the 6.0L Powerstroke, one must first analyze the factory benchmarks established by International Navistar and Ford. Throughout its production run from 2003 to 2007, the 6.0L maintained a consistent peak horsepower rating of 325 HP at 3,300 RPM. This high-RPM peak is a defining characteristic of the engine, distinguishing it from the lower-revving 7.3L predecessor and the later 6.4L and 6.7L platforms. This specific power curve allows the Super Duty to maintain momentum effectively during highway hauling and steep grade climbs.
The Evolution of Torque (560 to 570 lb-ft)
While horsepower remained static, torque output saw a minor but significant refinement. The 2003 and 2004 models were rated at 560 lb-ft of torque at 2,000 RPM. By 2005, through minor software refinements and hardware optimizations, Ford increased this rating to 570 lb-ft. This torque is generated through a robust physical foundation: a 3.74-inch bore and a 4.13-inch stroke, which creates a displacement that favors rapid cylinder pressure build-up without the excessive rotational mass found in larger-displacement engines. The 18.0:1 compression ratio further ensures that the engine maintains enough heat for efficient combustion under load, translating to immediate low-end grunt for F-250 and F-350 applications.
The Role of the HEUI System
The 6.0L utilizes a Hydraulic Electronic Unit Injection (HEUI) system, which uses highly pressurized engine oil to fire the fuel injectors. Unlike common-rail systems, the HEUI system allows for precise control over injection timing and pressure, which is central to maintaining the factory power curve. However, this reliance on oil pressure means that any degradation in oil quality or high-pressure oil pump (HPOP) performance will directly result in a drop in both horsepower and torque, often before the driver notices a mechanical failure.
Engineering the Torque Curve with the Garrett VGT Turbocharger
One of the most innovative features of the 6.0 Powerstroke is its Variable Geometry Turbocharger (VGT), manufactured by Garrett. This technology was revolutionary for the light-duty truck market in 2003, as it solved the age-old compromise between a small turbo for quick spooling and a large turbo for high-end power. By using an electronic actuator to move internal vanes within the exhaust housing, the 6.0L can effectively change the “size” of its turbo on the fly.
How VGT Technology Delivers Instant Power
When you accelerate from a standstill, the VGT vanes close to create a narrower passage for exhaust gases. This increases exhaust velocity and spins the turbine wheel faster, providing immediate boost and eliminating the “turbo lag” common in fixed-geometry setups. As RPMs rise, the vanes open up to allow maximum exhaust flow, preventing excessive backpressure and allowing the engine to reach its 325 HP peak at 3,300 RPM. This dynamic adjustment is why a stock 6.0L Super Duty can achieve 0-60 mph times in the 8.0 to 8.5-second range, which was exceptionally quick for a heavy-duty truck in the mid-2000s.
The 2003 model year features a 10-blade turbine wheel that produces the signature high-pitched whistle. Later models (2004-2007) moved to a 13-blade design to reduce noise for a more consumer-friendly experience. While the 10-blade turbo is often sought after for its sound, both provide similar performance metrics in stock form.
Real-World Scenario: Towing and Backpressure
Imagine towing a 12,000-lb fifth-wheel trailer up a 6% grade. In this scenario, the VGT system is constantly modulating to maintain optimal boost. If the vanes become “stuck” due to carbon buildup—a common pitfall of the 6.0L—the engine will either struggle to spool (low-end power loss) or over-boost at high RPM (risking head gasket failure). Professional maintenance of the VGT actuator and ensuring the engine reaches operating temperature regularly are critical for preserving the torque peak at 2,000 RPM.

Reliable Modifications to Increase 6.0 Powerstroke Horsepower
While the factory numbers are respectable, the 6.0L is widely considered one of the most “tunable” diesel engines ever produced. Because it was over-engineered in certain areas and restricted in others for emissions compliance, high-quality aftermarket solutions can unlock massive gains. A trusted starting point for any performance build is professional-grade electronic tuning via platforms like SCT or EZ-LYNK.
Street/Tow Tune
Expect gains of approximately +50 to +65 HP. This focuses on shifting the torque curve lower and improving transmission shift points for towing stability.
Race/Performance Tune
Aggressive fuel mapping can net up to +150 HP and +250 lb-ft of torque on stock injectors, transforming the truck into a high-performance machine.
The Critical Role of FICM Tuning
The Fuel Injection Control Module (FICM) is the “brain” of the 6.0L’s fuel system. Standard factory programming is often conservative, leading to sluggish throttle response and cold-start issues. Professional FICM tuning (such as the Hercules or Atlas tunes) improves fuel atomization and increases low-end torque. A healthy FICM should maintain a steady 48V; any drop below 45V indicates a failing unit that will significantly hamper horsepower output.
When increasing horsepower through tuning, Exhaust Gas Temperatures (EGTs) become your most critical metric. During sustained pulls or heavy towing, EGTs should never exceed 1,250°F. Sustained temperatures above this threshold risk melting pistons and damaging the VGT vanes.
To manage these increased temperatures, a 4-inch turbo-back exhaust system is considered the industry standard. This allows the engine to breathe, reducing backpressure and lowering EGTs by as much as 150-200 degrees while adding a modest 15-20 HP. When paired with a high-flow intake, you create the airflow foundation necessary for the engine to handle more aggressive fuel maps.
Maximizing Output with Injector and Turbocharger Upgrades
For owners looking to cross the 500-horsepower threshold, the factory 135cc injectors and stock turbocharger reach their physical limits. Moving into the “Stage 2” performance tier requires a synergistic approach where fuel volume is perfectly matched to air volume. If you provide too much fuel without enough air, you get excessive smoke and dangerous EGTs; too much air without fuel results in a sluggish, “laggy” truck.
Selecting Aftermarket Injectors
The most popular sizes for street-driven 6.0L trucks are 155/30s or 175/30s. The first number represents the total fuel capacity (cc), while the second represents the nozzle size percentage increase over stock.
- 155/30 Injectors: Ideal for heavy towing; supports roughly 450-475 rear-wheel horsepower (RWHP).
- 175/30 Injectors: The “sweet spot” for high-performance daily drivers; capable of supporting 525-550 RWHP when paired with a modified VGT turbo.
KC Turbos and VGT Upgrades
Trusted brands like KC Turbos have perfected the 6.0L turbocharger. A Stage 1 or Stage 2 KC VGT upgrade uses modern compressor wheel technology to move more Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM) of air than the factory unit. This allows you to burn the extra fuel from 175cc injectors cleanly. A 64mm VGT is a common choice for those seeking a broad powerband that still whistles like the original 2003 units but provides the flow necessary for 500+ HP.
By The Numbers: The 500 HP Build
Injector Size
Turbo Inducer
LB-FT Torque
Supporting the Fuel and Drivetrain
To ensure these injectors live a long life, a regulated return fuel system is highly recommended. The factory fuel rails on the 6.0L are “dead-headed,” meaning fuel can become trapped and hot at the back of the heads, leading to injector failure. A regulated return ensures consistent fuel pressure and flow to all eight injectors. Furthermore, once you exceed 500 HP, the 5R110 TorqShift transmission—while excellent—will require a professional rebuild with upgraded clutches and a heavy-duty torque converter to handle the massive torque loads.
Supporting Hardware: Protecting Quality Gains with Bulletproofing
Increased horsepower and torque are meaningless if the engine cannot stay together. The term “bulletproofing” refers to a comprehensive suite of hardware upgrades designed to address the 6.0L’s known failure points. When you increase boost and fuel, you also increase cylinder pressure. The factory Torque-to-Yield (TTY) head bolts are notorious for stretching under these conditions, leading to blown head gaskets.
📋
Step-by-Step Bulletproofing Guide
Replace factory TTY bolts with ARP 2000 studs, which offer 220,000 psi tensile strength to prevent head lift.
Install a high-quality oil cooler and an EGR cooler solution to prevent oil/coolant Delta T temperatures from exceeding 15 degrees.
Utilize an Edge Insight CTS3 to track vitals. Relying on factory “dummy” gauges is a recipe for disaster in a modified truck.
The High-Pressure Oil Pump (HPOP) Factor
Expert diesel technicians know that the 2003-2004.5 HPOP (swash-plate style) is more prone to failure than the later 2005-2007 gear-driven pumps. If you are building a high-horsepower early model, upgrading the HPOP to a reliable heavy-duty unit is essential for maintaining the high injection pressures required for aftermarket fuel nozzles. Without adequate oil pressure, your horsepower will plateau regardless of how large your injectors are.
✅ Pros of Modifications
- Superior towing ability on steep grades
- Better throttle response and drivability
- Increased fuel efficiency with professional tuning
- Significantly higher resale value for “bulletproofed” trucks
❌ Cons of Modifications
- Higher initial investment cost
- Increased wear on tires and drivetrain
- Strict maintenance schedules required
- Risk of component failure if tuned improperly
The 6.0 Powerstroke offers a solid foundation with 325 HP and 560-570 lb-ft of torque in its stock configuration. Significant power gains are achievable through high-quality tuning and VGT turbo optimizations, but longevity is only maintained by pairing these increases with professional “bulletproofing” hardware like ARP head studs. By understanding the intricate balance of air, fuel, and pressure within this engine, you can transform a misunderstood diesel into a trusted and reliable performance machine. For those looking to enhance their truck’s performance, start with a professional diagnostic check to ensure your baseline vitals—specifically oil and coolant temperatures—are healthy before installing high-output tuning.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the max safe horsepower for a stock 6.0 Powerstroke?
A stock 6.0 Powerstroke can safely handle approximately 400-430 rear-wheel horsepower with just a tuner. However, exceeding this level typically requires professional upgrades like ARP head studs to prevent head gasket failure, as the increased cylinder pressures of high-torque tunes will stretch the factory torque-to-yield bolts over time.
How does 6.0 Powerstroke torque compare to the 7.3 Powerstroke?
While the older 7.3L Powerstroke is renowned for reliability, the 6.0L produces more factory torque (560-570 lb-ft vs 500-525 lb-ft). Furthermore, the 6.0L engine utilizes a Variable Geometry Turbo which allows it to reach peak torque faster and maintain a broader power band than the fixed-geometry turbo found on the 7.3L.
Can I reach 600 horsepower with a 6.0 Powerstroke?
Yes, reaching 600 HP is achievable but requires a professional suite of modifications. This typically includes 190cc or larger injectors, a non-VGT or large S300/S400 frame turbocharger, a built 5R110 transmission, and a complete fuel system upgrade. Reliability at this level depends entirely on the quality of the components and the precision of the tuning.
Does a 4-inch exhaust increase HP and torque?
A 4-inch turbo-back exhaust typically adds 10-15 horsepower and reduces EGTs by 100-200 degrees. While the peak HP gain is modest, the primary benefit is the reduction in backpressure, which allows the turbo to spool faster, effectively shifting the torque curve lower in the RPM range for better towing performance.
Why is FICM tuning important for torque?
The Fuel Injection Control Module (FICM) manages the electrical impulse to the injectors. Expert FICM tuning improves the ‘inductive heating’ strategy and fuel timing, which results in significantly better low-end torque and throttle response. This is particularly noticeable in cold weather and during initial acceleration from a standstill.