Triton 4.6 L V8 4.6 Ford Engine Diagram: Step-by-Step Guide
The Triton 4.6 L V8 4.6 Ford engine diagram provides a detailed map of the intake manifold, ignition coils, and fuel rail locations. It highlights the modular design used in F-150s and Mustangs, helping you locate sensors and vacuum lines. This visual guide is essential for accurate part identification during maintenance or performance upgrades.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides a visual layout of the SOHC or DOHC modular Ford engine architecture
- The COP (Coil-on-Plug) ignition system is a critical identification point
- Always disconnect the battery before working near sensitive ECU connections
- Use the diagram to trace vacuum leaks that often cause rough idling
- Refer to this map when performing spark plug changes or sensor replacements
Whether you are performing a routine tune-up or tackling a complex timing chain replacement, having a clear triton 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram is the foundation of any successful repair. The Ford 4.6L Triton is a cornerstone of the modular engine family, powering millions of trucks, SUVs, and sedans with a reputation for longevity and steady performance. However, because this engine features an overhead cam design and a complex network of sensors and vacuum lines, it can be intimidating to the uninitiated. This guide provides a comprehensive visual and technical breakdown of the engine’s architecture, helping you identify critical components, understand the relationship between various systems, and troubleshoot issues with the confidence of a professional technician.
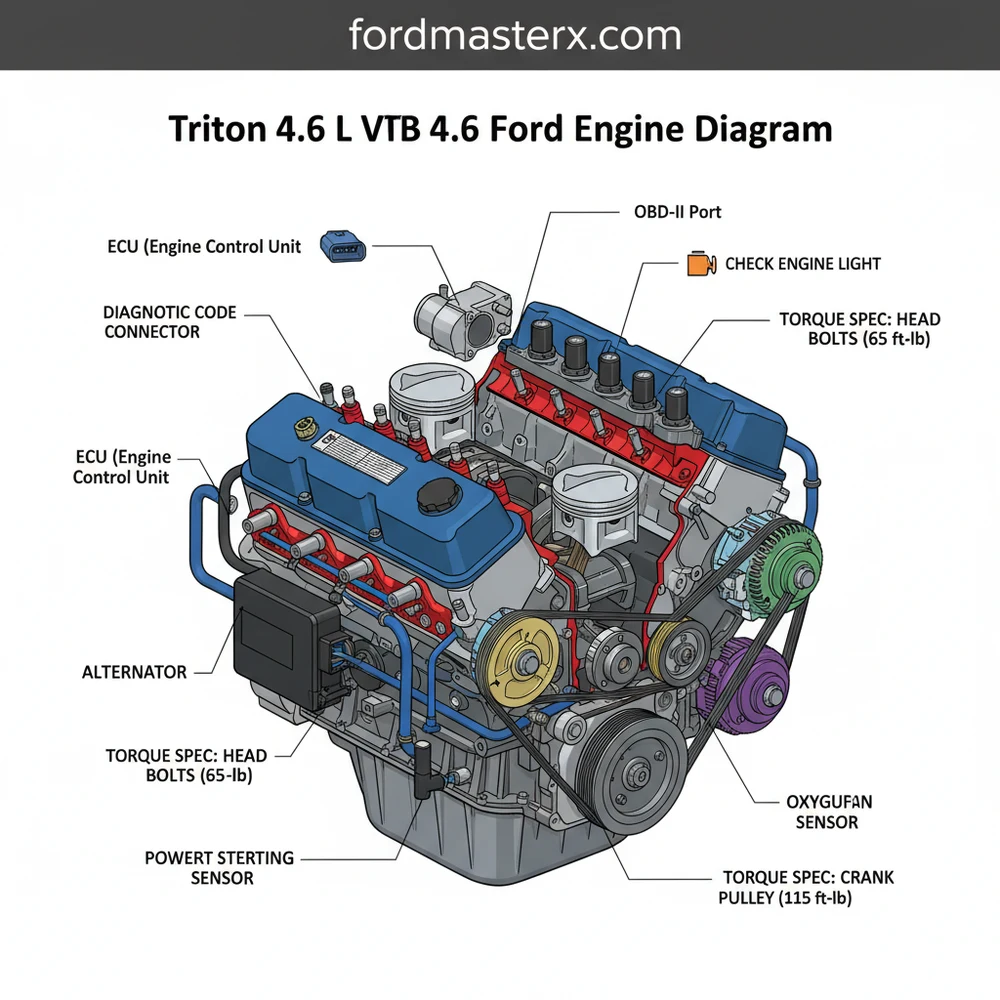
Decoding the Triton 4.6 L V8 4.6 Ford Engine Diagram
To effectively use a triton 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram, you must first understand the primary layout of this modular powerhouse. The engine is typically divided into several key zones: the top end (intake and ignition), the front end (accessory drive and timing), and the cooling system.
At the very top of the diagram, you will find the intake manifold, which houses the fuel rails and the individual fuel injectors. Below this, the diagram highlights the Coil-on-Plug (COP) ignition system. Unlike older engines with a central distributor, the 4.6L uses an individual coil for each spark plug, a design that is central to how the ECU (Engine Control Unit) manages combustion efficiency.
The front of the engine diagram is dominated by the accessory belt routing. This includes the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and the water pump. Behind the front timing cover, which is often represented in an “exploded view,” lies the complex timing chain system. This system consists of two separate chains, guides, and hydraulic tensioners that keep the camshafts synchronized with the crankshaft.
The 4.6L Triton comes in two primary configurations: the 2-valve (2V) and the 3-valve (3V) versions. While the bottom end remains similar, the top-end diagrams differ significantly regarding the intake manifold shape and the presence of Variable Cam Timing (VCT) solenoids on the 3V models.
How to Interpret and Use the Engine Diagram

Reading an automotive diagram requires a systematic approach. It is not just about finding a part; it is about understanding how that part interacts with the rest of the machine. Follow these steps to master the triton 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram during your next project.
- Orient Your Perspective: Most diagrams are drawn from the “front of vehicle” perspective. This means “Left” (Bank 2) is the driver’s side and “Right” (Bank 1) is the passenger side. Always verify your orientation before removing components like oxygen sensors or ignition coils to ensure you are working on the correct cylinder bank.
- Trace the Accessory Belt Path: Locate the tensioner pulley on the diagram. In a 4.6L Ford, the accessory belt must follow a specific serpentine path to provide the correct surface tension for the alternator and water pump. If the belt is routed incorrectly, you may experience overheating or a battery that won’t charge.
- Map the Coolant Flow: Identify the thermostat housing and the upper/lower radiator hoses. Understanding the coolant flow is vital for bleeding air out of the system. The 4.6L is known for trapping air pockets in the heater core and the back of the cylinder heads, which can lead to localized hot spots.
- Identify Sensor Locations: Use the diagram to find critical sensors like the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor, the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS), and the Crankshaft Position Sensor. These sensors feed data to the ECU to manage the air-fuel ratio.
- Locate Vacuum Lines: Vacuum leaks are a common cause of rough idling. Use the diagram to trace lines from the PCV valve and the brake booster back to the intake manifold plenum.
When using a diagram for timing chain repairs, ensure the engine is at Top Dead Center (TDC) on cylinder one. Failing to align the timing marks exactly as shown in the diagram can result in catastrophic valve-to-piston contact in this interference engine.
Troubleshooting with the 4.6L Diagram

When your check engine light illuminates, the triton 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram becomes a diagnostic roadmap. By connecting an OBD-II scanner to the port under the dashboard, you can retrieve a diagnostic code that points toward a specific component.
For example, a P0301 code indicates a misfire in cylinder number one. By referring to the engine diagram, you can quickly locate cylinder one (the front-most cylinder on the passenger side) and inspect the corresponding Coil-on-Plug and spark plug.
Common issues that the diagram helps resolve include:
- ✓ Spark Plug “Blowouts”: On earlier 2V models, the spark plug threads were shallow. The diagram helps you identify the torque spec requirements for ensuring these remain seated.
- ✓ Intake Manifold Leaks: Plastic intake manifolds are prone to cracking near the thermostat housing. The diagram shows the mounting bolt sequence required to seal the new gasket properly.
- ✓ Timing Chain Noise: If you hear a “slapping” sound at the front of the engine, the diagram will help you identify the location of the hydraulic tensioners which may have failed due to low oil pressure.
Pro Tips for Maintenance and Longevity
To keep your 4.6L Triton running for 300,000 miles or more, adherence to specifications and quality parts is non-negotiable. The triton 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram is only as good as the parts you put back into the vehicle.
Always use a torque wrench when installing spark plugs or intake manifold bolts on the 4.6L engine. The aluminum heads are fragile; over-tightening can strip threads, while under-tightening can lead to the infamous spark plug ejection issue. Always check the specific torque spec for your vehicle’s year.
Regarding the cooling system, maintaining proper coolant flow is essential. This engine is sensitive to electrolysis and corrosion if the coolant is not flushed every 50,000 to 100,000 miles. Use the diagram to identify the block drain plugs for a complete flush, rather than just draining the radiator.
Furthermore, the ECU relies on clean signals. Ensure your battery terminals are free of corrosion and that the grounding points, often indicated on a comprehensive wiring and engine diagram, are tight and clean. A poor ground can trigger multiple phantom diagnostic codes that are difficult to track down.
Conclusion: Mastering Your Triton 4.6L Engine
The triton 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram is more than just a picture of parts; it is an essential piece of equipment for any Ford owner. By understanding the relationship between the ECU, the ignition system, and the mechanical timing, you can transition from basic oil changes to advanced engine diagnostics and repair. Whether you are clearing a check engine light or replacing a worn accessory belt, always keep your diagram handy and respect the technical specifications provided by the manufacturer. With the right information and a methodical approach, the 4.6L V8 will continue to be one of the most reliable and hard-working engines in your garage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is the ECU located?
In most Ford vehicles using the 4.6L Triton, the ECU is mounted on the passenger-side firewall inside the engine bay. It manages fuel injection and timing. If your check engine light is on, this unit processes sensor data to generate a specific diagnostic code for troubleshooting performance or electrical issues.
What does this Triton engine diagram show?
The diagram illustrates the physical arrangement of the cylinder heads, intake plenum, and accessory drive belt routing. It identifies critical components like the throttle body, fuel injectors, and EGR valve, allowing owners to visualize how various systems interconnect for better diagnostic accuracy and significantly faster home repair times.
How many spark plugs and coils does it have?
The Ford 4.6L Triton V8 features eight spark plugs and eight individual ignition coils (Coil-on-Plug). Each cylinder has its own dedicated coil controlled by the ECU. When replacing these, ensure you follow the specific torque spec for the spark plugs to prevent thread damage in the aluminum heads.
What are the symptoms of a bad 4.6L sensor?
Common symptoms include a persistent check engine light, decreased fuel economy, or engine misfires. Using an OBD-II scanner will reveal a diagnostic code pointing to issues like a faulty MAF sensor or O2 sensor. This diagram helps you locate the specific faulty part for cleaning or full replacement.
Can I replace the intake manifold myself?
Yes, replacing the intake manifold is a common DIY task on the 4.6L Triton. You will need to remove the fuel rail and ignition coils first. Ensure you have the correct torque spec for the manifold bolts and follow a specific tightening sequence to prevent future coolant leaks.
What tools do I need for engine diagnostics?
For basic diagnostics, you need a socket set, torque wrench, and an OBD-II code reader. A torque wrench is vital to meet the exact torque spec for various bolts, while the scanner helps identify the specific diagnostic code triggered when the ECU detects a system malfunction or sensor failure.







