How To Reset Service Advancetrac: Diagnostic Procedures And System Restoration
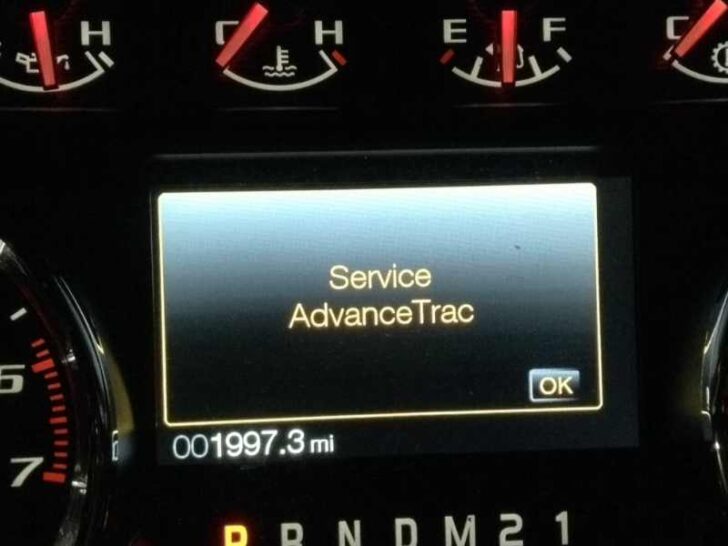
The sudden appearance of the “Service AdvanceTrac” warning on your dashboard doesn’t just deactivate your traction control—it compromises the sophisticated stability systems that keep your vehicle on its intended path. When this warning light illuminates, owners are often left with disabled safety features and a vehicle that may feel less responsive during emergency maneuvers, frequently caused by transient software glitches or sensor interference. This guide provides a professional-grade walkthrough on how to reset the AdvanceTrac system, ranging from simple ignition cycles to advanced OBD-II software restoration and hardware maintenance. By understanding the underlying architecture and following these diagnostic protocols, you can effectively clear the fault and ensure your vehicle’s safety parameters are fully operational.
Understanding the AdvanceTrac System and Error Indicators
📤 Share Image
AdvanceTrac is not a single component but a sophisticated integration of three primary safety subsystems: the Electronic Stability Control (ESC), the Traction Control System (TCS), and the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS). These modules work in a symbiotic relationship to monitor vehicle trajectory and wheel slip. If the system detects a discrepancy between the driver’s intended path (monitored by the steering wheel) and the actual vehicle direction (monitored by yaw rate sensors and wheel speed sensors), it intervenes by modulating engine torque and applying individual brake pressure.
By The Numbers
Data Scans Per Second
Transient Error Rate
The “Service AdvanceTrac” warning illuminates when the primary control module fails to receive valid data from its peripheral sensors or when there is a breakdown in the Controller Area Network (CAN bus) communication. This system monitors vehicle direction and wheel speed at a rate of 100 times per second. Any delay in this data transmission, even for a millisecond, can trigger a fail-safe mode, disabling the system to prevent unintended braking interventions.
In high-torque vehicles like the Ford F-150 or the Explorer, heavy towing or aggressive off-road driving often induces temporary sensor “blindness.” For instance, if you are stuck in deep mud or snow, the extreme variance in wheel speeds can confuse the logic gate, leading to a “ghost” warning. Differentiating these momentary glitches from persistent hardware failures—such as a snapped wire or a failed Steering Angle Sensor (SAS)—is the first step in a successful fresh start for your vehicle’s computer.
Performing a Soft Reset and Ignition Cycle to Restore Default Parameters
Before diving into hardware removal or deep software coding, it is essential to attempt a soft reset. Data suggests that approximately 30% of AdvanceTrac warnings are transient and can be resolved through a basic power cycle. These glitches often occur after a jump-start or when a battery is nearing the end of its life, causing a low-voltage state that prevents modules from initializing correctly during startup.

📋
AdvanceTrac Soft Reset Protocol
Turn the ignition to ‘On’ (without starting), wait 10 seconds, then turn ‘Off’. Repeat this three times. This forces the ECU to re-poll all sensors and can clear non-persistent fault codes.
Start the engine. While in Park, turn the steering wheel all the way to the left until it hits the lock, then all the way to the right. Return to the center. This re-calibrates the Steering Angle Sensor (SAS) ‘zero point’.
Drive the vehicle for at least 5 miles at speeds above 30 MPH. The system requires consistent wheel speed data across a range of speeds to validate that the ‘Service’ light can remain off.
Additionally, check the fuse box for the ABS and ESC fuses. If the fuse is partially seated or corroded, the module will suffer from intermittent power drops, triggering the light. Ensure all fuses meet factory-spec amperage. A clean, constant power delivery is the foundation of the AdvanceTrac system; without it, any software reset will fail immediately.
Hard Resetting via Battery Disconnection and Capacitance Discharge
When a soft reset fails, it usually indicates that the fault has been written to the Keep Alive Memory (KAM). This volatile memory stores “learned” behaviors and short-term error codes. To reboot the system entirely and restore factory defaults, you must perform a hardware-level power discharge. This is particularly effective after a battery swap or when the vehicle has been jump-started, which can leave residual “dirty” voltage in the capacitors of the ABS module.
Modern Ford vehicles require approximately 20 minutes of power deprivation to fully clear the KAM. Simply disconnecting the battery for 30 seconds is insufficient for modern high-capacitance modules.
To perform a comprehensive factory reset, follow this protocol:
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Optional but Recommended: Use a jumper wire to connect the disconnected positive and negative battery cables together (ensure they are nowhere near the battery posts). This creates a path for residual energy stored in capacitors to drain safely.
- Wait 20 to 30 minutes. This ensures the volatile memory in the ABS and PCM modules is completely erased.
- Reconnect the terminals, tightening them to factory torque specs to prevent vibration-induced voltage drops.
NEVER touch a jumper wire to the actual battery terminals. You are only connecting the vehicle’s disconnected wire leads to drain the system’s internal capacitors.
Once power is restored, the vehicle will need to undergo a “Relearn” procedure. The throttle body and AdvanceTrac system will be in their factory default states. Start the engine and let it idle for 5 minutes without touching the throttle; this allows the PCM to map the idle air trim. Then, perform the steering lock-to-lock procedure mentioned in Section 2 to initialize the SAS with the fresh memory state.
Utilizing OBD-II Diagnostics for a Fresh Start Software Reset
If the “Service AdvanceTrac” light persists, you must move beyond manual resets and interface directly with the vehicle’s internal software. Many “generic” scanners can clear check engine lights but fail to communicate with the ABS/Stability module. To achieve a fresh start, you need a tool capable of reading Manufacturer Specific (P1-series) codes and performing module-level resets.
The industry-standard software for Ford vehicles is FORScan, used in conjunction with an ELM327 adapter. This allows you to perform a “Module Reset” on the ABS module specifically. It is important to distinguish between “Clearing Codes” (which just deletes the error history) and “Resetting the Module” (which force-restarts the software within the module itself). If you have recently performed a brake job or replaced a caliper, you may also need to initiate an ABS Service Bleed through the software to remove trapped air that could be causing pressure discrepancies, preventing a successful restore of the AdvanceTrac system.
✅ Pros of Software Reset
- Pinpoints exact sensor failure
- Calibrates SAS precisely to zero
- Resets module communication logic
- Saves hours of physical diagnostic time
❌ Cons of Software Reset
- Requires specific OBD-II hardware
- Risk of “bricking” if power is lost
- Doesn’t fix physical wiring breaks
- Steep learning curve for software
Cleaning and Maintaining Hardware to Prevent Recurring Warnings
If a reset works but the light returns within a few miles, you are likely dealing with a “dirty” signal. The Wheel Speed Sensors (ABS sensors) operate using magnetism. Over time, metallic brake dust and road debris accumulate on the sensor tip. A single millimeter of metallic buildup on an ABS sensor can result in a 20% variance in speed reading accuracy. This inaccuracy causes the AdvanceTrac system to see “implausible data,” triggering an immediate shutdown.
Clean Sensor Faces
Remove sensors and wipe with a microfiber cloth and electronics cleaner to ensure a clean signal path.
Tone Ring Inspection
Inspect the magnetic rings for cracks or missing teeth. A cracked ring will cause a rhythmic signal drop.
Furthermore, the wiring harness near the front control arms is a common failure point. Constant suspension travel can cause wires to fray or develop internal breaks. Inspect the connectors for the “green crust” (verdigris) that indicates moisture intrusion. Applying a small amount of dielectric grease to these connectors during reassembly ensures a weatherproof, high-conductivity connection, providing the system with the fresh start it needs to maintain stability control over the long term.
In summary, resetting the Service AdvanceTrac system is a multi-tiered process. Start with non-invasive resets like the steering lock-to-lock cycle and ignition reset. If those fail, utilize a battery disconnect for a comprehensive factory default restoration. Finally, address the physical root cause by cleaning sensors and checking the harness for electrical integrity. If the ‘Service AdvanceTrac’ warning persists after these reset procedures, perform a full diagnostic scan using a tool capable of reading Ford-specific ABS and ESC codes to pinpoint hardware failure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it safe to drive while the Service AdvanceTrac light is on?
While the vehicle remains mechanically drivable, the stability and traction control systems are deactivated. This increases the risk of skidding or loss of control during adverse weather or emergency maneuvers. You should restore the system to its factory operating state as soon as possible to ensure maximum safety.
Will disconnecting the battery always reset the AdvanceTrac system?
A battery disconnect acts as a hard reset for the vehicle’s Keep Alive Memory (KAM), which can clear temporary software errors. However, if there is a permanent hardware fault, such as a severed sensor wire or a failed ABS pump, the AdvanceTrac warning will return immediately upon the next system self-test.
Why does my Service AdvanceTrac light come on only when I turn the steering wheel?
This typically indicates a failing Clock Spring or a Steering Angle Sensor (SAS) that has lost its calibration. In this scenario, a software reset is necessary to restore the ‘zero-point’ calibration of the sensor so the ECU accurately understands the steering wheel’s position relative to vehicle travel.
Can low brake fluid trigger an AdvanceTrac warning?
Yes, because AdvanceTrac relies heavily on the ABS hydraulic control unit. If fluid levels are low or there is air in the system, the module may detect a pressure variance and disable the system. Checking and cleaning the fluid reservoir is a critical step in providing a fresh start for the system.
What is the average cost to professionally reset the AdvanceTrac system?
A professional diagnostic reset typically costs between $100 and $150 at a dealership. This usually includes a full scan and recalibration of the steering angle sensor. If you have an OBD-II tool and software like FORScan, you can perform this restoration yourself for the cost of the interface cable.