Ford Ranger Fuse Box Diagram: Identification Guide
The 2001 Ford Ranger fuse box diagram identifies two primary panels: the passenger compartment fuse panel behind the side cover on the driver’s side dashboard and the power distribution box in the engine compartment. These charts label specific fuses for components like the radio, fuel pump, and headlights to ensure fast troubleshooting.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Identify both the cabin and engine compartment fuse locations.
- Recognize fuses protecting the ECU and fuel delivery systems.
- Never use a fuse with an incorrect amperage rating.
- Utilize the diagram to resolve a persistent check engine light.
- Keep the diagram handy for fast roadside electrical repairs.
Navigating the electrical system of a classic pickup can be a daunting task, but having a clear 2001 ford ranger fuse box diagram is the first step toward regaining control over your vehicle’s functionality. Whether you are dealing with a dead radio, a flickering dashboard, or a stubborn engine that refuses to turnover, the fuse box is often the source of both the problem and the solution. This comprehensive guide is designed to help Ford Ranger owners identify fuse locations, understand the specific ratings for each circuit, and learn how to troubleshoot electrical faults with confidence. By the end of this article, you will be equipped with the knowledge to perform basic electrical repairs, saving you time and money on diagnostic fees while ensuring your truck remains reliable on the road.
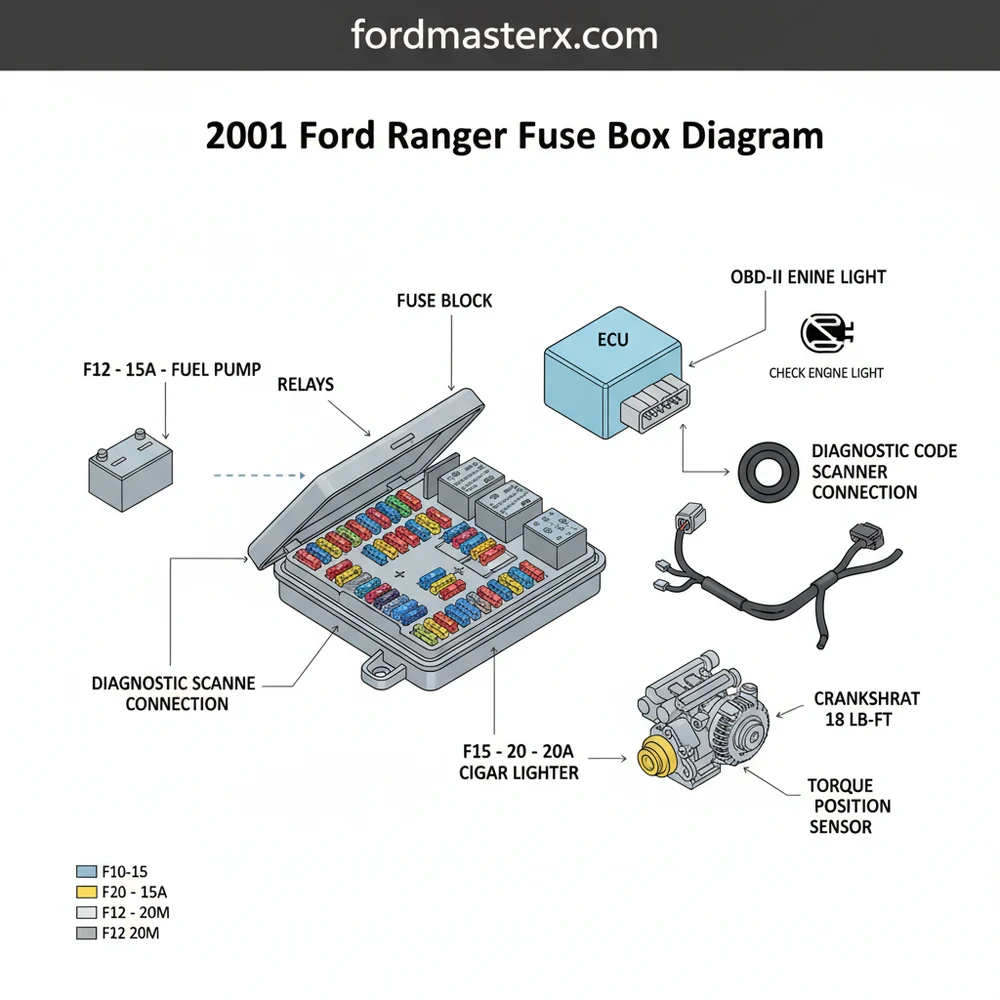
Understanding the 2001 Ford Ranger Fuse Box Layout
The 2001 Ford Ranger utilizes a dual-component electrical protection system consisting of the Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel and the Power Distribution Box located in the engine bay. The internal panel, situated on the driver’s side end of the instrument panel, handles lower-amperage accessories like the interior lights, instrument cluster, and the power windows. In contrast, the under-hood Power Distribution Box manages high-current circuits, including the starter motor, fuel pump, and the ECU (Engine Control Unit). Understanding these two distinct areas is vital because a failure in one can often mimic symptoms of the other.
In the 2001 model year, Ford utilized a mix of Mini-fuses and Maxi-fuses, alongside high-current relays. The diagram typically uses a numerical grid system to identify each slot. For instance, the interior panel usually contains 30 to 40 fuse slots, while the engine bay box houses large square relays and heavy-duty fuses. The diagram also accounts for variations between the 2.3L, 3.0L, and 4.0L engine configurations, as certain relays for components like the cooling fan or A/C compressor might shift positions depending on the powertrain. Knowing your specific engine type is essential for cross-referencing the labels found on the underside of the fuse box covers.
The fuse for the OBD-II diagnostic port is frequently shared with the cigarette lighter or auxiliary power point. If your code scanner won’t power up, check fuse #17 in the passenger compartment panel.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER – 2001 Ford Ranger Fuse Box Diagram showing Passenger Compartment and Engine Bay Layouts]
Step-by-Step Guide: Interpreting and Replacing Fuses

To effectively use the 2001 ford ranger fuse box diagram, you must follow a systematic approach to ensure safety and accuracy. Electrical work, even at the fuse level, requires precision to avoid damaging sensitive electronic components like the ECU or causing a short circuit that could lead to more significant repairs.
Step 1: Locate the Fuse Panels
Begin by identifying the two primary locations. The interior fuse panel is hidden behind a plastic cover on the side of the dashboard. Open the driver’s door and look at the side of the dash that touches the door when closed. Pull the cover off to reveal the fuses. The second location is the Power Distribution Box, found in the engine compartment near the battery. It is a black plastic box with a snap-on lid.
Step 2: Identify the Symptoms
Before pulling fuses, correlate your vehicle’s symptoms to the diagram. If your check engine light is on but you cannot retrieve a diagnostic code because the scanner won’t turn on, you are likely looking for a fuse related to the “Data Link Connector” or “Cigar Lighter.” If the engine cranks but won’t start, the fuel pump relay in the engine bay box is a primary suspect.
Step 3: Access and Inspect
Use a fuse puller tool—usually found inside one of the fuse box covers or purchased cheaply at an auto parts store—to remove the suspect fuse. Hold the fuse up to a light source. A healthy fuse has an unbroken metal “S” or “U” shape inside. If the metal link is broken or the plastic is charred, the fuse is blown.
Step 4: Check Amperage Ratings
Fuses are color-coded based on their amperage. It is critical to match the replacement fuse to the exact rating specified in the diagram. Using a 30-amp fuse in a 10-amp slot can cause the wiring to overheat before the fuse blows, potentially leading to a fire. Common colors include Red (10A), Blue (15A), Yellow (20A), and Clear/White (25A).
Never bridge a blown fuse with aluminum foil or a wire. This bypasses the safety mechanism and can result in a total harness meltdown or damage to the vehicle’s computer systems.
Step 5: Test the Circuit
Once the new fuse is installed, test the component. If the fuse blows again immediately, you have a “hard short” in the wiring. This indicates that a wire is touching the chassis or another wire, and further investigation into the wiring harness is required. If the fuse holds, the problem may have been a temporary surge.
Step 6: Resetting Systems
After replacing a major fuse (like one for the ECU), you may notice the truck idles strangely for a few miles. This is normal, as the computer is re-learning its operating parameters. If the check engine light persists, you may need to use an OBD-II scanner to clear any stored codes that were triggered during the electrical failure.
Common Electrical Issues and Troubleshooting
The 2001 Ford Ranger is known for a few specific electrical quirks that can be solved by consulting the fuse box diagram. One frequent complaint is the loss of instrument cluster lights or tail lights. These are often linked to a single fuse in the passenger compartment. If you find that your wipers work but only on one speed, or the “Park” function doesn’t work, the wiper relay in the engine bay box is the likely culprit.
Another common issue involves the OBD-II system. When a technician tries to read a diagnostic code and finds no power at the port, it is almost always due to a blown fuse in the interior panel. Because this circuit is shared with the 12V power outlet, using cheap phone chargers can often pop the fuse, inadvertently disabling your vehicle’s diagnostic capabilities. Additionally, if you experience a sudden drop in engine performance or the engine dies unexpectedly, check the ECU power relay. While the mechanical aspects like the timing chain or accessory belt might be intact, a lack of power to the computer will simulate a mechanical failure.
Keep a printed copy of the 2001 ford ranger fuse box diagram in your glovebox. Digital versions are great, but if your battery is dead and your phone is out of charge, a physical copy is a lifesaver.
Maintenance Tips and Best Practices
Maintaining the electrical health of your 2001 Ford Ranger goes beyond just replacing fuses. To prevent future issues, ensure that the battery terminals are clean and tightened to the correct torque spec. Loose terminals cause voltage spikes that can blow sensitive fuses or damage the alternator. Periodically inspect the engine bay fuse box for signs of moisture or corrosion, which can interfere with the coolant flow sensors or the transmission control solenoids.
- ✓ Check Grounds: Ensure the ground wires attached to the chassis are rust-free to prevent “ghost” electrical issues.
- ✓ Dielectric Grease: Use a small dab of dielectric grease on relay pins to prevent oxidation in humid climates.
- ✓ Correct Amperage: Always verify the fuse rating twice; a 15A fuse should never be replaced with a 20A fuse.
- ✓ Inspect Hardware: While under the hood, check your accessory belt for cracks, as a failing belt can hinder the alternator’s ability to charge the system.
If you encounter a problem that the 2001 ford ranger fuse box diagram cannot solve—such as a persistent check engine light despite all fuses being intact—it may be time to look at mechanical components. For example, issues with coolant flow might be related to a thermostat rather than a fan relay, or a noise from the front of the engine could indicate the timing chain needs attention rather than an electrical sensor. However, by mastering the fuse box, you eliminate the simplest variables first, allowing for a more logical and cost-effective approach to vehicle maintenance. Keep your Ranger running strong by respecting its electrical limits and performing routine inspections of its vital fuse panels.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is the 2001 Ford Ranger fuse box located?
The interior 2001 Ford Ranger fuse box is located on the driver’s side of the dashboard, accessible by removing the side cover panel. A second high-power distribution box is found under the hood, situated on the driver’s side inner fender well near the battery for easy access during maintenance.
What does the 2001 Ford Ranger fuse box diagram show?
This diagram shows the layout of both the passenger compartment and engine bay fuse panels. It identifies the amperage rating and specific electrical component for every fuse and relay, including power for the ECU and accessories, helping you locate the exact circuit needing repair or testing.
How many connections does the fuse box have?
The fuse box connects to the main battery feed via a heavy-gauge cable secured with a specific torque spec to prevent arcing. Internally, each fuse socket has two metal terminals that complete the circuit between the power bus bar and the individual wiring harness for that specific vehicle component.
What are the symptoms of a bad fuse?
Symptoms of a bad fuse include non-functional electrical components like the radio or wipers. If the fuse for the OBD-II port or ECU fails, you might experience a no-start condition or a check engine light that refuses to clear despite fixing the underlying mechanical issue in the truck.
Can I replace a 2001 Ford Ranger fuse myself?
Replacing a fuse is one of the easiest DIY tasks on a 2001 Ford Ranger. As long as you follow the diagram and use the correct amperage, you can safely restore power to your electronics without professional help, saving significant time and money on basic electrical diagnostics.
What tools do I need for fuse troubleshooting?
To properly service your fuse box, you will need a small fuse puller tool, often found inside the box cover. A digital multimeter or test light is essential for checking continuity, and an OBD-II scanner helps if a blown fuse triggered a specific diagnostic code in the system.






