Ford Focus Serpentine Belt Diagram: Step-by-Step Guide
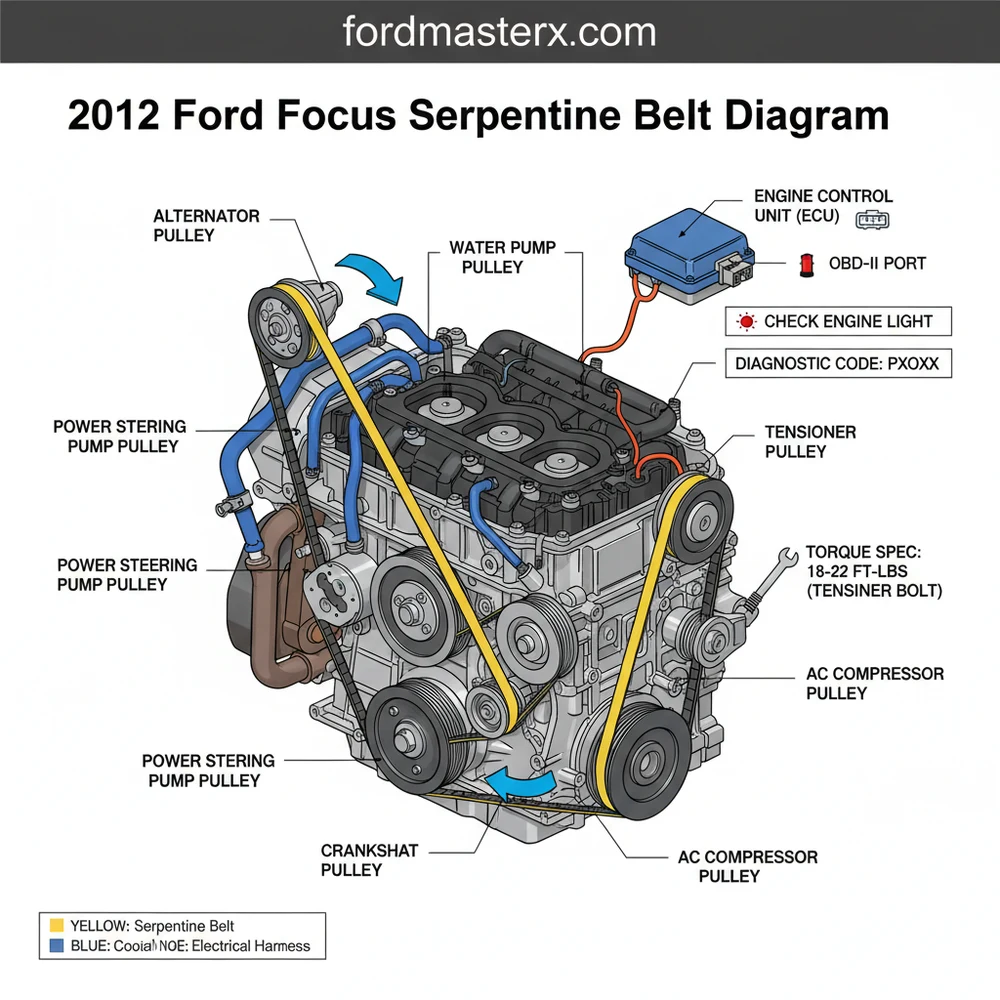
The 2012 Ford Focus serpentine belt diagram illustrates the routing path around the crankshaft, alternator, A/C compressor, and tensioner. To install, follow the loop starting at the crankshaft, wrapping under the tensioner, and over the alternator. Correct routing prevents slippage and ensures all engine accessories function correctly without damaging internal components.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Visualizes the exact routing path for the multi-ribbed belt.
- Identifying the automatic tensioner is crucial for belt release.
- Ensure the belt is fully seated in pulley grooves to avoid damage.
- Use the diagram to verify routing before starting the engine.
- Essential when replacing worn belts or servicing the alternator.
Maintaining the heart of your vehicle’s accessory system requires precision, and having a clear 2012 ford focus serpentine belt diagram is the first step toward a successful repair. Whether you are dealing with a persistent squeal under the hood or performing routine preventative maintenance, understanding how the accessory belt weaves through the various pulleys is essential for ensuring your alternator, air conditioning, and water pump function correctly. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of the routing path, the tools required for the job, and the technical specifications needed to keep your Focus running smoothly. You will learn how to identify each component, the proper way to release tension, and how to troubleshoot common issues that may arise during the installation process.
Understanding the 2012 Ford Focus Serpentine Belt Diagram
The 2012 Ford Focus, specifically those equipped with the 2.0L Ti-VCT GDI engine, utilizes a specific layout for its accessory drive system. When looking at a 2012 ford focus serpentine belt diagram, you will notice that the belt connects several critical components to the crankshaft pulley, which provides the rotational energy needed to power them. Unlike older vehicles that may have used multiple V-belts, this modern serpentine system uses a single, long “ribbed” belt to manage most tasks, though some configurations involve a secondary “stretch-fit” belt specifically for the A/C compressor.
The primary diagram features a series of circles representing the pulleys. At the bottom, the largest pulley is the crankshaft. Moving upward and toward the front of the vehicle, you will find the alternator (generator), which maintains the electrical charge for the ECU and battery. Nearby sits the water pump pulley, which is vital for maintaining consistent coolant flow throughout the engine block to prevent overheating. The diagram also illustrates the position of the tensioner pulley and the idler pulley. The tensioner is a spring-loaded arm designed to apply a specific amount of pressure to the belt, ensuring it does not slip under load.
( ALT ) ( WP )
O O
/ \ / \
(TEN) O \ / O (IDL)
\ \ / /
\ \ / /
\ ( CRK ) /
\_O_/
LEGEND:
CRK: Crankshaft (Drive Pulley)
ALT: Alternator
WP: Water Pump
TEN: Tensioner Pulley
IDL: Idler Pulley
Figure 1: Typical routing for the 2.0L Ti-VCT Main Accessory Belt
In this configuration, the “ribbed” side of the belt always contacts the ribbed pulleys (like the alternator and crankshaft), while the “smooth” back side of the belt typically contacts the idler or tensioner pulleys. Visualizing this distinction is crucial; if the belt is installed inside-out or routed on the wrong side of a pulley, it will suffer immediate damage and potentially cause the belt to snap, leading to a loss of power steering and cooling.
The 2012 Ford Focus often uses a dual-belt system. The main belt drives the alternator and water pump, while a separate, smaller stretch-fit belt drives the A/C compressor. The main 2012 ford focus serpentine belt diagram focus is usually on the larger, tensioned belt.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
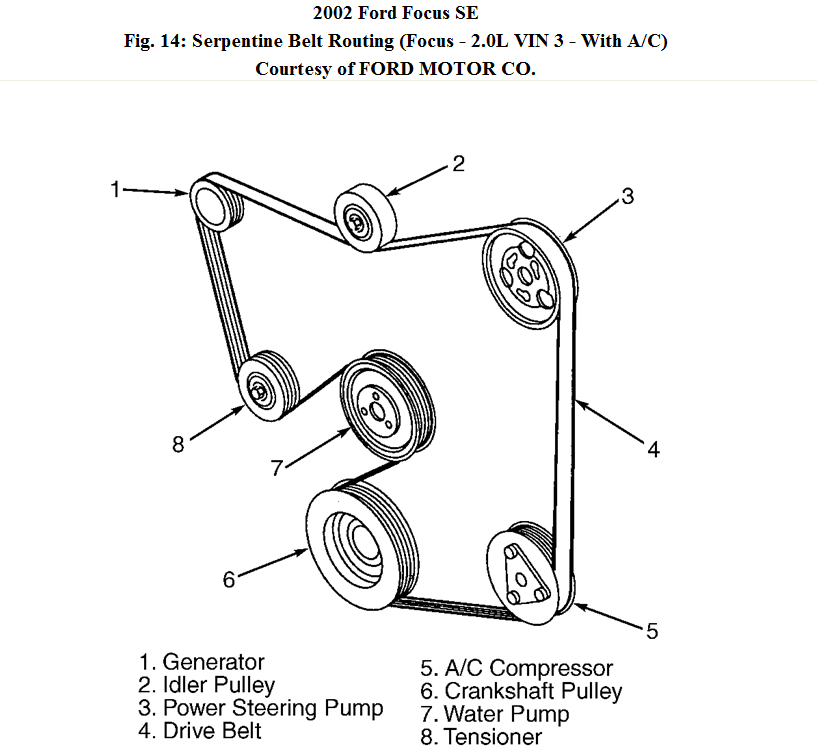
Replacing the belt using the 2012 ford focus serpentine belt diagram requires patience and the right set of tools. Because the engine bay in the Focus is relatively compact, you will likely need to access the pulleys through the passenger-side wheel well.
Never attempt to service the serpentine belt while the engine is running or while the ignition is in the ‘ON’ position. Ensure the engine is completely cool to avoid burns from the nearby engine block or radiator hoses.
To interpret and apply the diagram correctly, follow these steps:
- Preparation and Access: Park the vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake. Jack up the front passenger side and secure it with a jack stand. Remove the passenger-side front wheel and the plastic inner fender splash shield. This provides a direct line of sight to the crankshaft and tensioner.
- Locate the Tensioner: Find the automatic belt tensioner. On the 2012 Focus, this is usually located between the crankshaft and the alternator. It features a 14mm or 15mm bolt head (or a square drive hole) used to rotate the arm.
- Release Tension: Using a long-handled wrench or a dedicated serpentine belt tool, rotate the tensioner bolt clockwise (or as indicated by the specific tensioner design) to compress the spring. This will create slack in the belt.
- Remove the Old Belt: While holding the tensioner in the compressed position, slip the belt off the uppermost pulley (usually the alternator). Slowly release the tensioner arm and then finish unthreading the belt from the remaining pulleys.
- Inspect the Pulleys: Before installing the new belt, spin the water pump, alternator, and idler pulleys by hand. They should spin freely without grinding noises or “wobbling.” Check for oil leaks from the front main seal that might contaminate the new belt.
- Route the New Belt: Referencing your 2012 ford focus serpentine belt diagram, begin by wrapping the belt around the crankshaft pulley. Work your way up, ensuring the ribs of the belt seat perfectly into the grooves of the pulleys. Leave the tensioner or the easiest-to-reach pulley for the final step.
- Final Seating: Compress the tensioner again and slide the belt over the final pulley. Double-check that the belt is centered on every pulley and not hanging off the edge of any flange.
- Test the Installation: Briefly start the engine to ensure the belt tracks correctly. Observe the belt for any jumping or unusual vibrations.
Use a flashlight to inspect the “valleys” of the pulley ribs. Accumulated debris or old belt rubber can cause the new belt to chirp. A stiff nylon brush can be used to clean the grooves before installation.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting

When the serpentine belt fails or begins to wear out, the 2012 Ford Focus may exhibit several symptoms. The most common is a high-pitched squealing sound, especially during cold starts or when the A/C is turned on. This usually indicates a glazed belt or a failing tensioner that can no longer maintain the correct torque spec for belt pressure.
Another critical issue involves the “Check Engine Light.” If the belt slips significantly, the alternator may not provide consistent voltage to the ECU. This can trigger an OBD-II diagnostic code such as P0620 (Generator Control Circuit) or P0622. If the belt snaps entirely, you will lose coolant flow. Since the water pump is driven by this belt, the engine temperature will spike almost immediately. If you see the temperature gauge rising, pull over instantly to avoid warping the cylinder head.
It is also important to distinguish between the accessory belt and the timing chain. The 2012 Ford Focus 2.0L engine uses a timing chain, which is internal and lubricated by engine oil. While the serpentine belt is a routine maintenance item, the timing chain is designed to last the life of the engine, though it should be inspected if you hear metallic rattling from inside the timing cover.
Tips and Best Practices
To maximize the lifespan of your accessory belt and ensure the reliability of your Ford Focus, consider these professional recommendations:
- ✓ Inspect Every 60,000 Miles: While modern EPDM belts don’t crack as visibly as older neoprene belts, they do lose material. Use a belt wear gauge to check the depth of the ribs.
- ✓ Replace the Tensioner: It is often wise to replace the tensioner assembly at the same time as the belt. A weak internal spring can cause the new belt to wear prematurely.
- ✓ Check for Fluid Leaks: Oil or coolant leaks can significantly shorten the life of a serpentine belt. Ensure the water pump seal is intact to prevent coolant from slicking the belt surface.
- ✓ Use High-Quality Components: Stick with OEM or reputable aftermarket brands like Gates, Continental, or Dayco to ensure the belt matches the original dimensions and material specifications.
By following the 2012 ford focus serpentine belt diagram and adhering to these maintenance steps, you can avoid the inconvenience of a roadside breakdown. Proper belt tension and alignment are the keys to a quiet, efficient engine and a long-lasting charging and cooling system. Whether you are clearing an OBD-II code or simply performing a weekend tune-up, accuracy is your best tool for success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is the serpentine belt tensioner located?
The tensioner is located on the front of the engine block, usually positioned between the alternator and the crankshaft pulley. On the Ford Focus, you can access it more easily by removing the passenger-side wheel and splash shield. Use a long-handled wrench to rotate the tensioner arm and release belt tension.
What does the serpentine belt diagram show?
The diagram shows the specific sequence and direction the belt takes around various pulleys like the A/C compressor and water pump. It helps prevent incorrect installation, which could cause accessories to rotate backward or fail. It serves as a visual map for maintaining the engine’s accessory drive system.
What is the torque spec for the tensioner bolt?
While the belt itself doesn’t have a torque spec, the mounting bolt for the automatic tensioner typically requires a specific torque spec of approximately 18-22 lb-ft. If you notice a check engine light related to charging or cooling, use an OBD-II scanner to check for a specific diagnostic code.
What are the symptoms of a bad serpentine belt?
Common symptoms include squealing noises from the engine bay, visible cracking or fraying on the belt, and loss of power steering or air conditioning. If the belt slips significantly, the ECU may trigger a check engine light or a battery warning light due to insufficient alternator output.
Can I replace the serpentine belt myself?
Yes, replacing a serpentine belt is a manageable DIY task for most owners. By following the 2012 Ford Focus serpentine belt diagram, you can ensure the routing is correct. It requires basic hand tools and about 30-60 minutes of time, significantly saving on professional labor costs.
What tools do I need for belt replacement?
You will need a 15mm or 19mm long-handled wrench to release the tensioner. Additionally, a jack and jack stands are necessary to remove the passenger-side wheel for better access. A flashlight helps in confirming the belt is properly seated in all grooves before you start the engine.