Ford Focus Fuse Box Diagram: Quick Identification Guide
The 2010 Ford Focus fuse box diagram covers two main locations: the passenger compartment panel under the instrument panel and the engine compartment power distribution box near the battery. Using these layouts allows you to pinpoint fuses for the ECU, fuel pump, and OBD-II port to resolve electrical failures or a check engine light.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Identifies locations for both the interior and engine bay fuse panels
- Essential for locating the ECU and fuel pump protection circuits
- Always disconnect the battery before replacing high-amperage fuses
- Use the diagram to troubleshoot a non-responsive OBD-II port
- Refer to this guide when a specific electrical component fails to power
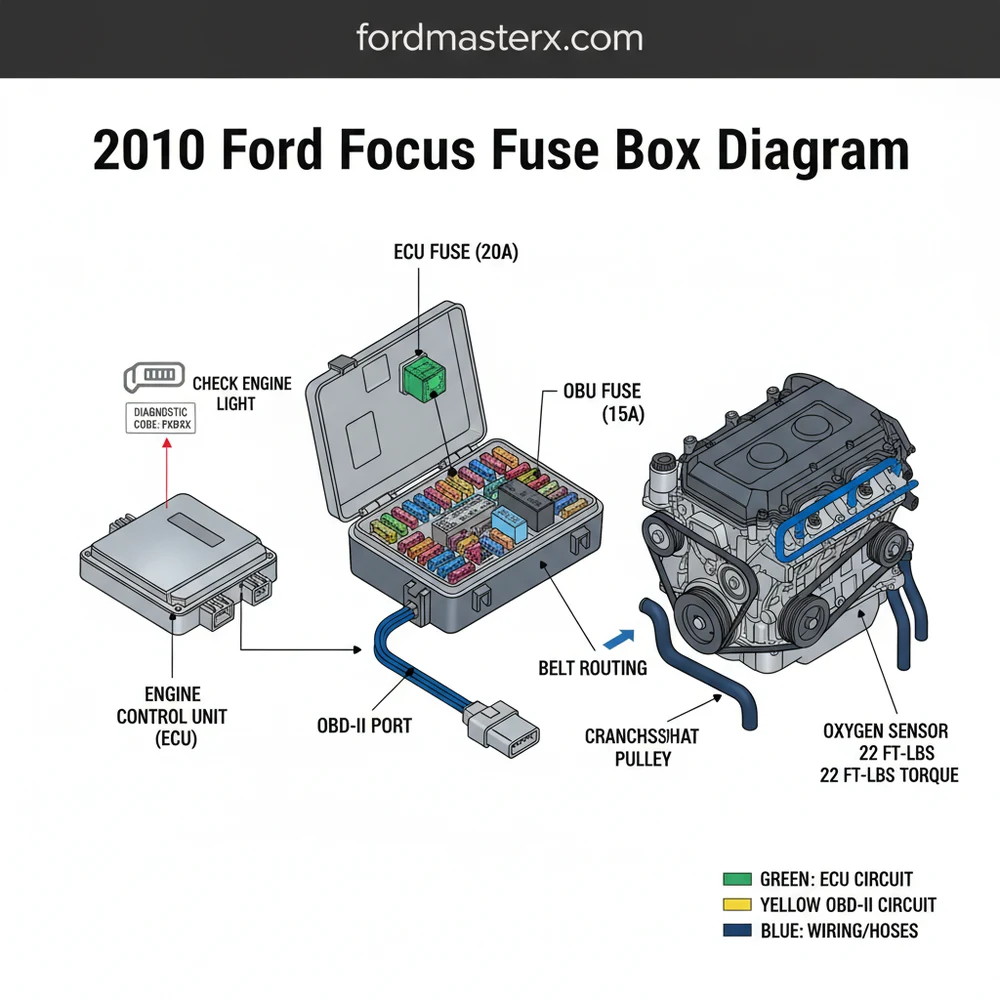
Finding yourself stranded with a non-responsive radio or a car that refuses to crank can be incredibly frustrating. For owners of the second-generation North American Focus, the 2010 ford focus fuse box diagram is the most critical document for resolving these common electrical gremlins. Whether you are dealing with a blown power outlet or a more serious issue involving the Engine Control Unit (ECU), understanding the layout of your vehicle’s protection system is the first step toward a successful repair. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of every fuse and relay, ensuring you can identify, test, and replace components safely and effectively.
Understanding the layout of your vehicle begins with recognizing that Ford utilized two distinct locations for electrical protection. The 2010 Ford Focus features a Passenger Junction Box (PJB) located inside the cabin and a Power Distribution Box (PDB) located under the hood. The interior diagram primarily covers convenience features like power windows, lighting, and the OBD-II diagnostic port. Conversely, the engine bay diagram focuses on high-current applications, including the cooling fan, starter motor, and the fuel pump. Each fuse is color-coded by amperage: for instance, 10A fuses are typically red, 15A are blue, and 20A are yellow.
The diagram itself is organized into a grid system. In the engine compartment, you will find larger “J-Case” fuses alongside standard mini-fuses and various relays. Relays are essentially remote-controlled switches that allow a small current to control a much larger one. If your accessory belt is spinning but the air conditioning compressor won’t engage, the culprit is often a faulty relay found in this engine bay box. Similarly, while the timing chain handles mechanical synchronization, the electrical sensors that monitor its position rely on stable power from the engine-side fuse box.
The interior fuse box is located behind a removable plastic panel on the lower right-hand side of the passenger-side footwell. The engine compartment fuse box is located near the battery on the driver’s side of the engine bay.
Interpreting the 2010 ford focus fuse box diagram requires a systematic approach. Follow these steps to diagnose and resolve electrical issues safely:
1. Safety First and Tool Selection: Before touching the electrical system, turn off the ignition and remove the key. If you are working on high-current fuses in the engine bay, it is often wise to disconnect the negative battery terminal. To re-secure the battery later, remember that the torque spec for the terminal nut is usually around 5-7 lb-ft; over-tightening can crack the battery post. You will need a fuse puller (often located inside the fuse box lid), a flashlight, and ideally, a digital multimeter.
2. Accessing the Panels: For the interior box, sit in the passenger seat and look for a small rectangular panel on the right side of the footwell. Pull the tab to release the cover. For the engine compartment box, lift the hood and locate the black plastic box near the driver-side fender. Squeeze the release tabs on the sides to lift the lid.
3. Locating the Specific Fuse: Look at the underside of the fuse box cover or refer to your digital 2010 ford focus fuse box diagram. Each slot is numbered. For example, if your OBD-II scanner won’t power up, you should specifically look for the fuse labeled for the Data Link Connector or Cigar Lighter, as these often share a circuit.
4. Visual Inspection: Use the fuse puller to remove the suspected fuse. Hold it up to a light source. A healthy fuse has a continuous U-shaped wire inside. If the wire is broken or if there is a dark brown scorch mark inside the plastic casing, the fuse is blown and must be replaced.
5. The Multimeter Test: Sometimes a fuse looks fine but is still faulty. Set your multimeter to the Continuity setting (the symbol that looks like a sound wave). Touch the two probes to the tiny metal test points on the top of the fuse while it is still installed. If the meter beeps, current can flow through it. If it remains silent, the fuse is dead.
6. Matching Amperage: Never replace a fuse with one of a higher amperage rating. If the diagram calls for a 15A fuse, do not use a 20A fuse. Doing so can cause the wiring to overheat before the fuse blows, potentially leading to a vehicle fire.
7. Verifying the Fix: Once the new fuse is installed, restore power to the vehicle. If the component works, the repair is complete. However, if the fuse blows again immediately, you have a short circuit in that specific system, and further diagnostic work is required.
8. Clearing Codes: If the blown fuse was related to the ECU or a critical engine sensor, you might see a check engine light even after the repair. Use an OBD-II scanner to read the diagnostic code and clear it from the system memory.
Never use a screwdriver or metal pliers to remove fuses without disconnecting the battery. You risk shorting out the entire junction box, which can damage the ECU and result in a very expensive repair.
Many 2010 Ford Focus owners encounter issues where a blown fuse is merely a symptom of a larger problem. For instance, if you experience poor coolant flow and the engine begins to overheat, you might immediately suspect the water pump. However, it is equally likely that the fuse for the electric cooling fan has failed, preventing the radiator from shedding heat. Similarly, if your car displays a check engine light with codes related to “system lean,” check the fuel pump relay before assuming the pump itself has failed.
The OBD-II port is another common failure point. If your mechanic cannot connect their scanner to retrieve a diagnostic code, the fuse for the “Cigar Lighter/Power Point” is often the culprit. This is a very common issue on the 2010 model. If the fuse is intact but the system still fails, you may be looking at a ground wire issue or a fault within the ECU itself. If you notice smoke, a burning plastic smell, or if multiple unrelated electrical systems fail at once, seek professional help immediately, as this indicates a major wiring harness failure.
Always keep a small assortment of spare mini-fuses (5A, 10A, 15A, 20A) and a dedicated fuse puller in your glovebox. It can turn a potential tow-truck situation into a five-minute roadside fix.
To keep your Ford Focus running smoothly, maintenance should extend beyond the accessory belt and oil changes. Periodically inspecting your fuse boxes can prevent oxidation and corrosion, especially in the engine compartment where moisture and salt can penetrate. Use a dedicated electrical contact cleaner if you notice any white or green powdery residue on the fuse terminals.
When purchasing replacement parts, opt for high-quality fuses from reputable brands. Cheap, unbranded fuses can sometimes fail to blow at their rated amperage, putting your entire electrical system at risk. Furthermore, if you are performing any work that involves moving components like the timing chain or serpentine belt, ensure that no wiring harnesses are pinched or rubbing against moving parts, as this is a frequent cause of intermittent “ghost” electrical issues that are difficult to track down.
- ✓ Match Amperage Exactly: Always verify the color and number on the fuse against the diagram.
- ✓ Inspect Relays: If a fuse is fine but the part still doesn’t work, swap the relay with a known good one (like the horn relay).
- ✓ Clean Terminals: Ensure the fuse seats firmly in its slot to prevent arcing and heat buildup.
- ✓ Document Changes: If you add aftermarket accessories, use an “add-a-circuit” kit rather than tapping directly into existing wires.
In summary, having a clear and accurate 2010 ford focus fuse box diagram is an essential part of any DIY toolkit. By understanding how to navigate both the interior and engine-side panels, you can diagnose everything from a minor accessory failure to a major engine management issue. Remember to follow safety protocols, use the right tools, and always investigate the root cause if a fuse continues to blow. With these tips and the detailed breakdown provided, you are well-equipped to handle the electrical needs of your Ford Focus and keep it on the road for years to come.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the Ford Focus Fuse Box Diagram: Quick Identification Guide
Identify the electrical symptom – Determine which component is failing to narrow down the specific fuse search.
Locate the appropriate fuse panel – Refer to the 2010 ford focus fuse box diagram for either the interior or engine bay panel.
Understand the circuit mapping – Match the component name to the fuse number provided in the diagram legend.
Verify the fuse integrity – Remove the fuse and check for a broken filament or use a multimeter to test for continuity.
Connect a new fuse – Insert a replacement fuse with the exact same amperage rating to restore the circuit safely.
Complete the repair – Restart the vehicle and use a scanner to clear any diagnostic code or check engine light triggers.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is the 2010 Ford Focus fuse box located?
The vehicle features two fuse boxes. The passenger compartment fuse panel is located under the driver’s side dashboard, behind a removable plastic cover. The high-power distribution box is situated in the engine compartment, typically on the driver’s side near the battery, protected by a plastic lid that unclips.
What does the fuse box diagram show?
The diagram illustrates the layout and numbering of every fuse and relay. It provides a legend that maps each number to a specific circuit, such as the ECU, headlights, or power windows. It also specifies the correct amperage rating for each fuse to prevent electrical fires or damage.
How many connections does the Ford Focus fuse box have?
The engine compartment box features several dozen fuse slots and large relay terminals. It connects the battery to major systems like the ECU via heavy-gauge wiring. Ensure the terminal mounting bolts are tightened to the correct torque spec to maintain a reliable connection and avoid voltage drops or arcing.
What are the symptoms of a bad fuse box or blown fuse?
If a check engine light appears but your scanner cannot pull a diagnostic code, the OBD-II port fuse may be blown. Other symptoms include dead accessories, a radio that won’t turn on, or the engine failing to start because the ECU or fuel pump relay has lost power.
Can I replace a fuse in the Ford Focus myself?
Yes, replacing a fuse is a simple DIY task. After consulting the 2010 ford focus fuse box diagram to find the correct location, use a fuse puller to remove the suspect fuse. If the internal metal wire is broken, simply insert a new fuse of the identical amperage.
What tools do I need for fuse box maintenance?
You will need a plastic fuse puller, which is often found inside the fuse box cover, and a digital multimeter for testing continuity. If you are replacing the entire box or heavy-duty relays, a socket set is required to ensure the mounting hardware meets the manufacturer’s torque spec.







