Ford 6.2 Firing Order Diagram: Quick Reference Guide
The Ford 6.2L V8 firing order is 1-3-7-2-6-5-4-8. On this engine structure, cylinder 1 is at the front passenger side, followed by 2, 3, and 4. The driver side contains cylinders 5, 6, 7, and 8 from front to back. This layout is vital for correct ignition timing.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Visualizing the sequence for ignition timing and wire routing.
- Identifying cylinder number one at the passenger-side front.
- Ensuring spark plug wire integrity to prevent engine misfires.
- Using this map when replacing spark plugs or ignition coils.
- Referring to the diagram during fuel system or timing repairs.
Working with a high-displacement engine like the Ford 6.2L V8 requires precision, especially when performing ignition system maintenance or diagnosing a rough idle. Understanding the ford 6.2 firing order diagram is the first step toward ensuring your truck operates at peak efficiency. This diagram provides the essential blueprint for the sequence in which each cylinder ignites, which is critical for timing, power delivery, and engine longevity. Whether you are replacing spark plugs, ignition coils, or diagnosing a persistent misfire, having the correct schematic allows you to visualize the internal system and avoid costly mistakes. In this guide, you will learn the exact cylinder layout, the specific ignition sequence, and how to apply this knowledge to your DIY repairs or professional diagnostics.
The Ford 6.2L engine, often referred to as the Boss V8, utilizes a unique two-spark-plug-per-cylinder configuration. This means that while the firing order remains a single sequence, the ignition system manages sixteen separate spark events per cycle.
Understanding the Ford 6.2 Firing Order Diagram and Layout
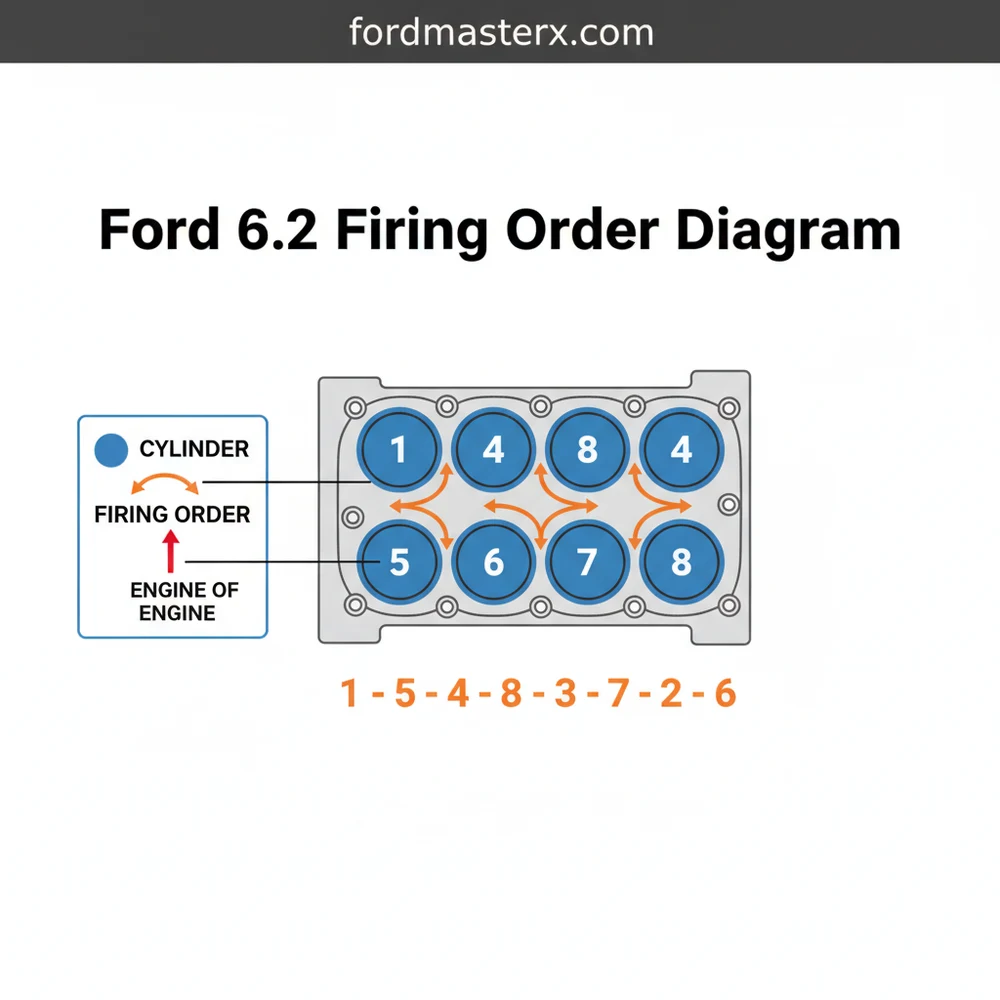
The technical configuration of the Ford 6.2L V8 is designed for heavy-duty performance, and its layout is consistent across various Super Duty applications. To read the diagram correctly, you must first identify the cylinder structure. Unlike some manufacturers that alternate numbers from side to side, Ford uses a sequential numbering system for each bank.
The primary sequence for this engine is 1-5-4-8-6-3-7-2. This order determines the exact moment the powertrain control module (PCM) sends a signal to the ignition coils to fire. The schematic for this system displays two distinct banks of four cylinders. As you stand in front of the vehicle looking at the engine, the passenger side is Bank 1, and the driver side is Bank 2.
FRONT OF VEHICLE (Radiator Side)
————————-
(Bank 2) (Bank 1)
[5] [1]
[6] [2]
[7] [3]
[8] [4]
————————-
REAR OF VEHICLE (Firewall Side)
FIRING ORDER: 1-5-4-8-6-3-7-2
In this schematic, Bank 1 (Passenger Side) contains cylinders 1, 2, 3, and 4, starting from the front of the engine and moving toward the firewall. Bank 2 (Driver Side) contains cylinders 5, 6, 7, and 8, also starting from the front. The visual breakdown of these elements is crucial because the dual-plug system means each cylinder has a primary coil-on-plug (COP) and a secondary wire that leads to the second spark plug. Misidentifying a cylinder location can lead to “phantom” misfires where you replace parts on the wrong side of the engine.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Apply the Ford 6.2 Firing Order Diagram

Correctly interpreting the diagram and applying it to your vehicle requires a methodical approach. Follow these steps to ensure you are working accurately within the ignition system.
- 1. Locate Cylinder One: Begin by identifying cylinder one. This is the front-most cylinder on the passenger side of the vehicle. This serves as your starting point for the entire firing order sequence.
- 2. Map the Remaining Cylinders: Following the physical layout, count back on the passenger side (1, 2, 3, 4). Then, move to the front-most cylinder on the driver side to find cylinder 5, counting back to 8 at the firewall.
- 3. Disconnect and Secure: Before working on the ignition system, disconnect the negative battery terminal. Because the 6.2L uses high-energy coils, preventing accidental discharge or short circuits is a vital safety precaution.
- 4. Identify the Dual-Plug System: Locate the primary coil atop the cylinder and the secondary wire leading to the side of the cylinder head. Ensure you are not confusing the secondary wire of one cylinder with the primary coil of another.
- 5. Trace the Sequence: If you are troubleshooting a timing issue, trace the 1-5-4-8-6-3-7-2 order. This is the path the electrical pulse follows. If you find wires crossed between cylinder 4 and 8, for example, the engine will experience severe vibration and loss of power.
- 6. Installation and Reassembly: When installing new components, always work on one cylinder at a time. This prevents mixing up the harnesses or secondary wires. Refer back to the blueprint after every two cylinders to verify your progress.
Never attempt to swap coils while the engine is running. The Ford 6.2L ignition system carries high voltage that can cause serious injury or damage the vehicle’s sensitive electronic control modules.
To perform this work, you will typically need a 5/8-inch spark plug socket, a variety of extensions, a torque wrench, and perhaps a mirror to see the plugs located closer to the firewall. Because the 6.2L engine is physically large and tucked back into the engine bay in Super Duty trucks, patience is your most valuable tool.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with the Ignition System

When the firing order is disrupted or a component within the sequence fails, the 6.2L engine will exhibit specific symptoms. The most frequent problem is a localized misfire, often accompanied by a Check Engine Light (CEL). Using an OBD-II scanner, you may see codes ranging from P0301 to P0308. These codes correspond directly to the cylinder numbers in the diagram; for example, P0305 indicates a misfire in cylinder 5 (front of the driver side).
The blueprint helps you solve these issues by allowing you to “swap-test” components. If you have a P0301 code, you can swap the coil from cylinder 1 with the coil from cylinder 2. If the code changes to P0302, you have confirmed the coil is faulty. If the code remains P0301, the issue lies with the spark plug, the secondary wire, or the fuel injector for that specific cylinder.
Warning signs of a firing order or ignition problem include:
- ✓ Rough idling or “hunting” for RPMs at stoplights.
- ✓ Significant drop in fuel economy (MPG).
- ✓ Hesitation or “bucking” during heavy acceleration or towing.
- ✓ A strong smell of unburned gasoline from the exhaust.
If you experience backfiring through the intake or exhaust, this is a classic sign that wires have been crossed, and the firing order is out of sync. If the engine makes a loud rhythmic tapping or knocking sound that accompanies a misfire, seek professional help immediately, as this could indicate internal mechanical failure rather than a simple ignition oversight.
Tips and Best Practices for Maintaining the Ford 6.2L V8
Maintaining the integrity of your engine’s ignition system goes beyond just knowing the firing order. To ensure the longest life for your 6.2L Boss engine, follow these professional recommendations:
When replacing spark plugs, always use a small amount of dielectric grease on the inside of the coil boot. This prevents the rubber from sticking to the porcelain of the plug and creates a moisture-proof seal that prevents arcing.
First, always use high-quality components. The 6.2L is sensitive to spark plug gap and quality. Motorcraft OEM plugs are widely considered the best choice for this specific configuration. Ensure your spark plugs are gapped to the factory specification (typically 0.041–0.047 inches) before installation.
Second, pay attention to the secondary spark plug wires. Because this engine has two plugs per cylinder, the wires leading to the secondary plugs (located on the side of the head) are often overlooked. Over time, these wires can become brittle due to engine heat. Inspecting them for cracks or white “carbon tracking” can save you from mysterious misfires that occur only under heavy load.
Finally, adhere to a strict maintenance schedule. While modern spark plugs are rated for long intervals, the 6.2L often works hard in towing environments. Inspecting your coils and plugs every 60,000 to 75,000 miles can prevent the coils from working too hard to jump a wide gap, which ultimately saves you money by preventing premature coil failure. By keeping your ford 6.2 firing order diagram handy and following these best practices, you can maintain the power and reliability that Ford trucks are known for.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is the cylinder layout located?
On the Ford 6.2L engine, the cylinder configuration starts with cylinder one at the front of the passenger side. Cylinders one through four are on the passenger side (bank 1), while cylinders five through eight are located on the driver side (bank 2), starting from the front near the radiator.
What does the Ford 6.2 firing order diagram show?
The diagram illustrates the exact sequence in which each cylinder fires during a full engine cycle. It maps out the ignition system structure, helping mechanics ensure that spark plug wires or ignition coils are connected to the correct cylinders to maintain engine balance and prevent damaging backfires.
How many spark plugs does this engine system have?
The Ford 6.2L V8 is a unique system that utilizes two spark plugs per cylinder, totaling 16 plugs. This dual-plug configuration improves combustion efficiency and reduces emissions. When following the firing order diagram, ensure both plugs for each specific cylinder are firing correctly and in the proper sequence.
What are the symptoms of a bad firing order?
If the ignition wires or coils are installed incorrectly, you will experience severe engine misfires, rough idling, and significant power loss. You might also hear popping sounds from the intake or exhaust. Checking the diagram ensures the firing sequence component is aligned with the manufacturer’s specified layout.
Can I replace the spark plugs and coils myself?
Yes, replacing these components is a common DIY task. Using a firing order diagram makes it easier to track which wire goes to which cylinder. However, because there are 16 plugs, the layout can be complex, so take your time to avoid crossing any ignition connections or components.
What tools do I need for ignition system maintenance?
To work on the Ford 6.2L ignition system, you need a 5/8-inch spark plug socket, a variety of socket extensions, and a torque wrench. A gapping tool is also necessary to ensure each spark plug meets the specific configuration requirements before installation into the engine’s cylinder head structure.







