6.4 L 6.4 Powerstroke Engine Diagram: Identification Guide
The 6.4 L 6.4 Powerstroke engine diagram illustrates the layout of the twin-turbo system, fuel injectors, and vital sensors. It allows you to locate components when a check engine light appears, facilitating faster repairs. Use it to find wire routings to the ECU or verify specific torque spec requirements during assembly.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Maps out the complex twin-turbo and EGR systems for easier access.
- Helps identify sensor locations for rapid diagnostic code resolution.
- Essential for identifying high-pressure fuel system components and lines.
- Provides a visual guide for electrical routing from the engine to the ECU.
- Use this diagram during major engine overhauls or routine component swaps.
For any Ford truck enthusiast or diesel mechanic, navigating the engine bay of a Super Duty requires more than just a wrench; it requires a clear roadmap. The 6.4 l 6.4 powerstroke engine diagram serves as this essential guide, providing a visual breakdown of one of the most complex diesel engines ever put into a consumer pickup. Whether you are chasing a mysterious coolant leak or attempting to replace a worn accessory belt, understanding the spatial relationship between the twin turbochargers, the high-pressure fuel system, and the cooling circuits is vital. This article will deconstruct the primary engine diagram, explain how to interpret technical schematics for troubleshooting, and provide the specific specifications needed to keep your Powerstroke running at peak performance.
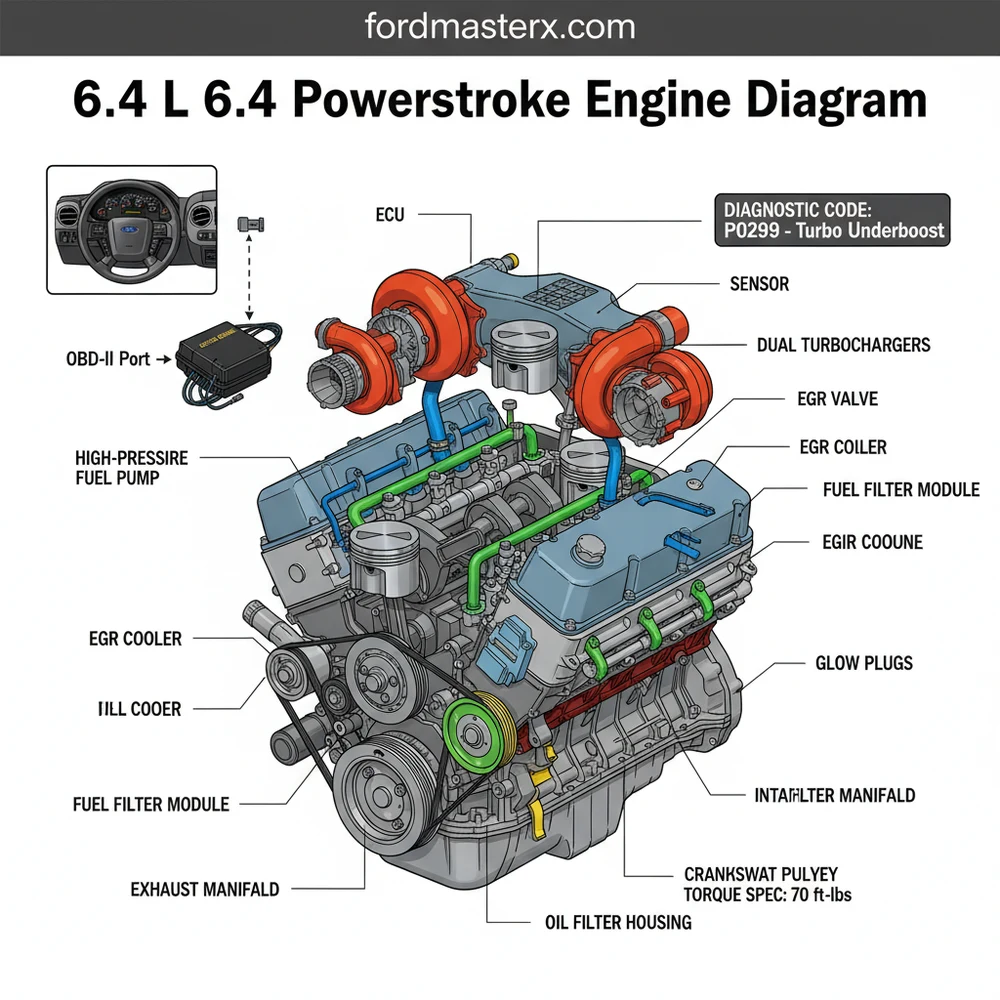
Decoding the 6.4 L 6.4 Powerstroke Engine Diagram
The 6.4-liter Powerstroke engine is a marvel of engineering, but its dense packaging can be intimidating. When you look at a comprehensive 6.4 l 6.4 powerstroke engine diagram, the first thing you will notice is the “V” configuration of the eight cylinders, topped by a sophisticated sequential twin-turbocharger system. Unlike its predecessors, the 6.4L utilizes a Compound Turbo setup, where a small high-pressure turbo provides low-end response and a larger low-pressure turbo handles high-end power. The diagram typically highlights these units at the top rear of the engine block.
Another critical element found in the diagram is the cooling system layout. The 6.4L is notorious for its heat production, requiring a massive radiator and a secondary cooling circuit. The diagram will trace the coolant flow from the water pump through the front cover, splitting paths to the EGR coolers and the oil cooler. You will also see the placement of the ECU (Engine Control Unit), which acts as the brain of the operation, mounted near the firewall to protect it from extreme engine heat while remaining accessible for wiring harnesses.
The fuel system is another core component of the visual breakdown. The diagram illustrates the path from the horizontal fuel conditioning module (HFCM) on the frame rail up to the high-pressure fuel pump (HPFP) located deep within the engine’s “valley.” Understanding this layout is crucial because the 6.4L uses a Common Rail injection system, which operates under extreme pressures. Most diagrams use color-coding—blue for low-pressure fuel and red for high-pressure lines—to help you distinguish between the supply and return sides of the system.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: A detailed 3D exploded view of the 6.4L Powerstroke engine showing the twin turbocharger assembly, EGR coolers, accessory belt drive, and fuel rail locations with labeled callouts for the ECU and water pump.]
Step-by-Step Guide to Reading and Applying the Diagram

Interpreting a technical engine diagram is a skill that bridges the gap between theory and successful repair. Follow these steps to use your 6.4 l 6.4 powerstroke engine diagram effectively for maintenance or component replacement.
Before beginning any work, ensure the engine is completely cool. The 6.4L Powerstroke retains heat significantly longer than smaller engines due to its massive iron block and dual turbo setup.
- Identify the Primary Orientation: Start by locating the front of the engine on the diagram, usually identified by the accessory belt and cooling fan. This allows you to distinguish between “Driver Side” (Left) and “Passenger Side” (Right) components, which is critical when identifying which cylinder head or exhaust manifold needs attention.
- Trace the Accessory Belt Path: Locate the serpentine belt routing on the diagram. On the 6.4L, the accessory belt drives the alternator, power steering pump, and A/C compressor. Use the diagram to identify the tensioner pulley location; you will need a long-reach breaker bar to release tension when replacing the belt.
- Locate the OBD-II Interface and ECU: If you are dealing with an electronic issue, use the diagram to find the wiring harness paths leading to the ECU. The OBD-II port, located under the dashboard inside the cabin, connects directly to this system. The diagram helps you understand which sensors (such as the EBP or MAP sensors) feed data back to the ECU to trigger specific behaviors.
- Analyze the Coolant Flow: Trace the lines from the degas bottle through the radiators. The 6.4L has two separate cooling systems in some configurations. Ensure you are looking at the primary circuit if you are troubleshooting an overheating issue. The diagram will show you exactly where the thermostats are located (inside the water outlet housing).
- Verify Torque Specs: Once you have identified the part on the diagram, consult the accompanying specification table for the correct torque spec. For example, the fuel injector hold-down bolts require precise tightening to prevent “black death” (carbon buildup) or fuel leaks.
- Locate Timing Components: While the 6.4L uses a gear-driven timing assembly rather than a traditional timing chain, the diagram is essential for aligning the camshaft and crankshaft marks during a major overhaul. Ensure the marks on the drive gears align perfectly as shown in the schematic.
High-pressure fuel lines on the 6.4L can retain pressure even after the engine is off. Never crack a fuel line while the engine is running or immediately after shutdown. Consult the diagram to find the pressure relief valves.
To perform these tasks, you will generally need a comprehensive set of metric sockets (8mm to 24mm), torque wrenches (both inch-pounds and foot-pounds), a scan tool capable of reading Ford-specific P-codes, and plenty of shop rags.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with the Diagram
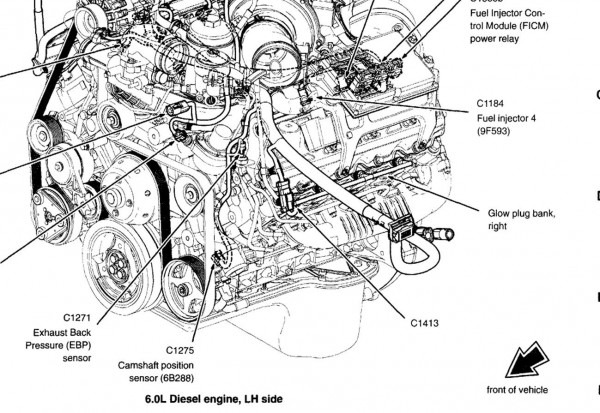
The 6.4L Powerstroke is known for specific “trouble spots” that can be easily identified once you know where to look on the diagram. One of the most frequent issues is the failure of the EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) coolers. By referencing the diagram, you can see that these coolers are located on the top of the engine. A leak here often results in white smoke from the exhaust or a disappearing coolant level without visible external drops.
When the check engine light illuminates, your first step should be connecting a scanner to the OBD-II port. If you receive a diagnostic code related to fuel pressure, use the diagram to find the fuel rail pressure sensor and the volume control valve on the HPFP. The diagram acts as a process of elimination; if the code points to a specific bank, you can narrow your search to the four injectors on that side of the engine.
- ✓ Oil Dilution: Check the diagram for the DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter) regeneration path; frequent “regens” can cause fuel to enter the crankcase.
- ✓ Turbo Lag: Inspect the actuator on the high-pressure turbo as identified in the diagram.
- ✓ Radiator Leaks: Look at the diagram for the mounting points of the primary radiator, which are prone to cracking due to frame flex.
If you find that your troubleshooting leads to a “piston wash” scenario or a “cracked piston,” which are catastrophic failures, the diagram will help you understand the extent of the teardown required, usually necessitating cab-off service.
Maintenance Tips and Best Practices
Maintaining a 6.4L Powerstroke is about prevention rather than reaction. Because the tolerances in the common rail system are so tight, clean fuel is your best defense against expensive repairs.
Always replace both fuel filters at the same time. The primary filter is on the frame rail, while the secondary is on top of the engine. Neglecting one will lead to premature failure of the high-pressure pump.
To ensure longevity, follow these best practices:
- ✓ Strict Oil Intervals: Change your oil every 5,000 miles. Use a high-quality 5W-40 or 15W-40 synthetic oil designed for diesel particulate filters.
- ✓ Cooling System Care: Use only Motorcraft Gold coolant (or a compatible ELC) and test the nitrite levels regularly. The diagram shows the complexity of the cooling path—cavitation in the front cover can lead to oil and coolant mixing.
- ✓ Battery Health: This engine requires immense cranking power. Always replace batteries in pairs. Weak batteries can damage the ECU and the fuel injection control logic over time.
- ✓ Observe Torque Specs: When performing any work, especially on the top end, use a torque wrench. Over-tightening a valve cover bolt or an intake manifold bolt can lead to vacuum leaks or cracked castings.
In conclusion, having a high-quality 6.4 l 6.4 powerstroke engine diagram is non-negotiable for anyone serious about DIY maintenance or professional repair of these trucks. By understanding how to read the cooling flow, identifying the electronics like the ECU, and knowing where to plug in for a diagnostic code, you can significantly extend the life of your engine. While the 6.4L has its quirks, it remains a powerhouse capable of immense work when cared for with the precision and knowledge that a proper diagram provides.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is the ECU located?
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) on a 6.4 Powerstroke is typically found on the driver-side firewall, protected by a plastic cover. This central hub manages all engine functions, and the diagram helps trace the wiring harnesses that connect to various sensors for proper diagnostic testing and electrical repair.
What does this engine diagram show?
This diagram provides a comprehensive visual map of the engine’s external components, including the twin-turbocharger setup, fuel rails, and cooling lines. It is designed to help technicians visualize the spatial relationships between parts when performing complex repairs or identifying fluid leaks deep within the engine valley.
How many fuel injectors does this engine have?
The 6.4 L Powerstroke features eight Piezo-electric fuel injectors located under the valve covers. Each injector is precision-controlled by the ECU and operates at extremely high pressures. Referring to the diagram ensures you identify the correct cylinder sequence when addressing a specific misfire diagnostic code or injector failure.
What are the symptoms of a bad EGR cooler?
Symptoms of a failing EGR cooler include white smoke from the exhaust, loss of coolant without visible leaks, and a check engine light. You may also see a P0401 diagnostic code. The engine diagram helps you locate the EGR assembly to inspect for soot buildup or internal moisture.
Can I replace the injectors myself?
Replacing injectors on a 6.4 L Powerstroke is a complex task that requires removing the valve covers and high-pressure fuel lines. While possible for advanced DIYers, it requires extreme cleanliness and a calibrated torque wrench to meet every specific torque spec for the fuel line connections to prevent leaks.
What tools do I need for diagnostics?
You need a high-quality OBD-II scanner to read stored codes and monitor live data from the ECU. Basic hand tools are required for component access, but specialized tools like a fuel pressure gauge and a high-range torque wrench are essential for accurate 6.4 L Powerstroke repair work.






