1999 Ford Explorer Oxygen Sensor Location
Last Updated on by Skylar Drift
In this informative article, I will provide valuable insights and actionable guidance on the location of the oxygen sensor in a 1999 Ford Explorer. Designed to cater to Ford vehicle owners, DIY enthusiasts, mechanics, and individuals interested in Ford vehicle maintenance, this content aims to help readers gain a comprehensive understanding of this crucial component in their vehicle. By incorporating structured data, relevant images, and a YouTube video, this article will explore the keyword intent in-depth, offering practical examples and case studies. With clear subheadings and bullet points, readers can easily navigate through the content, and a concise FAQs section will provide factual answers to common questions. For a professional and friendly tone, I will also include a call-to-action, guiding readers to further related content on the website.
Introduction
Welcome to this comprehensive guide on the 1999 Ford Explorer oxygen sensor location. In this article, I will provide valuable insights and actionable guidance to Ford vehicle owners, DIY enthusiasts, mechanics, and individuals interested in Ford vehicle maintenance.
Understanding the Purpose of Oxygen Sensors
What is an Oxygen Sensor?
An oxygen sensor, also known as an O2 sensor, is a crucial component of the vehicle’s emission control system. It is responsible for monitoring the level of oxygen in the exhaust gases and providing feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) to ensure optimal fuel-air mixture.
Why is an Oxygen Sensor Important in a Ford Explorer?
The oxygen sensor plays a vital role in the fuel efficiency, performance, and emissions of the Ford Explorer. It helps the ECU maintain the ideal air-fuel ratio, resulting in improved combustion and reduced emissions. A faulty oxygen sensor can lead to decreased fuel efficiency, poor performance, and potentially harmful emissions.
How Does an Oxygen Sensor Work?
Oxygen sensors utilize a chemical reaction between the oxygen in the exhaust gases and the sensor element to generate a voltage signal. This signal is then interpreted by the ECU to make adjustments to the fuel delivery system. The sensor can operate in different temperature ranges depending on its type.

Types of Oxygen Sensors
Heated Oxygen Sensor
A heated oxygen sensor is equipped with an internal heating element that allows it to reach operating temperature quickly. This type of sensor is commonly found in newer vehicles and provides more accurate readings during cold starts and low-temperature conditions.
Unheated Oxygen Sensor
Unheated oxygen sensors, also known as non-heated or standard oxygen sensors, do not have a built-in heating element. They rely on the heat generated by the exhaust gases to reach their operating temperature. These sensors are usually found in older vehicles.
Wideband Oxygen Sensor
Wideband oxygen sensors are more advanced and can accurately measure the air-fuel ratio over a wider range. They are commonly used in high-performance vehicles or vehicles with advanced engine management systems.
Signs of a Faulty Oxygen Sensor
Check Engine Light
One of the most common signs of a faulty oxygen sensor is the illumination of the check engine light on the vehicle’s dashboard. The ECU detects irregularities in the oxygen sensor readings and triggers the check engine light to alert the driver.
Decreased Fuel Efficiency
A faulty oxygen sensor can cause the engine to run rich or lean, leading to decreased fuel efficiency. If you notice a significant drop in your Ford Explorer’s miles per gallon, the oxygen sensor might be to blame.
Poor Performance
An oxygen sensor malfunction can negatively impact the overall performance of the vehicle. You may experience rough idling, engine misfires, or a noticeable lack of power.
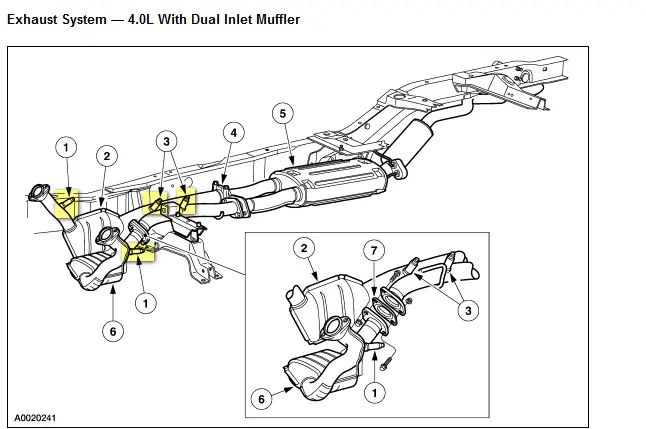
Locating the Oxygen Sensor in a 1999 Ford Explorer
Overview of the Oxygen Sensor Location
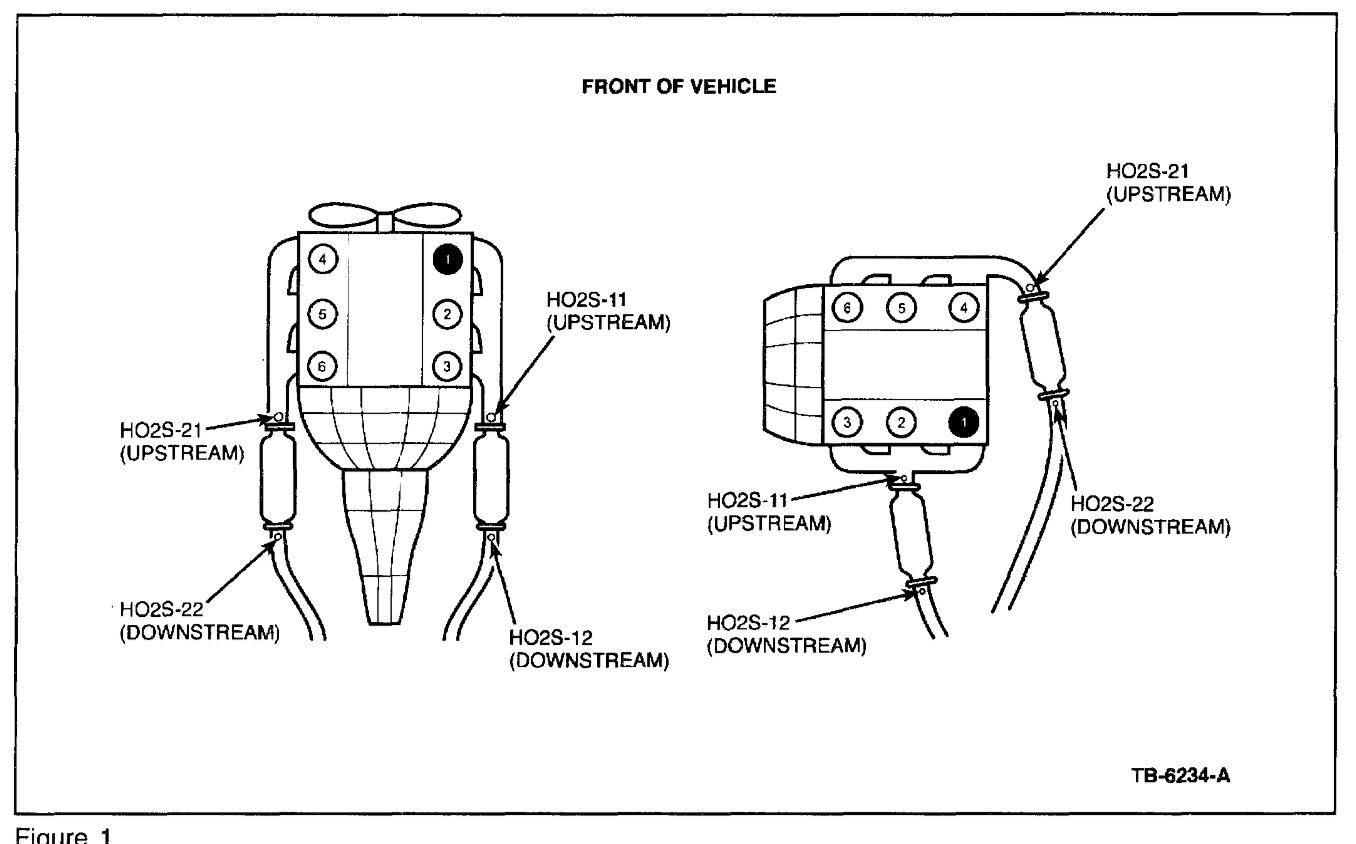
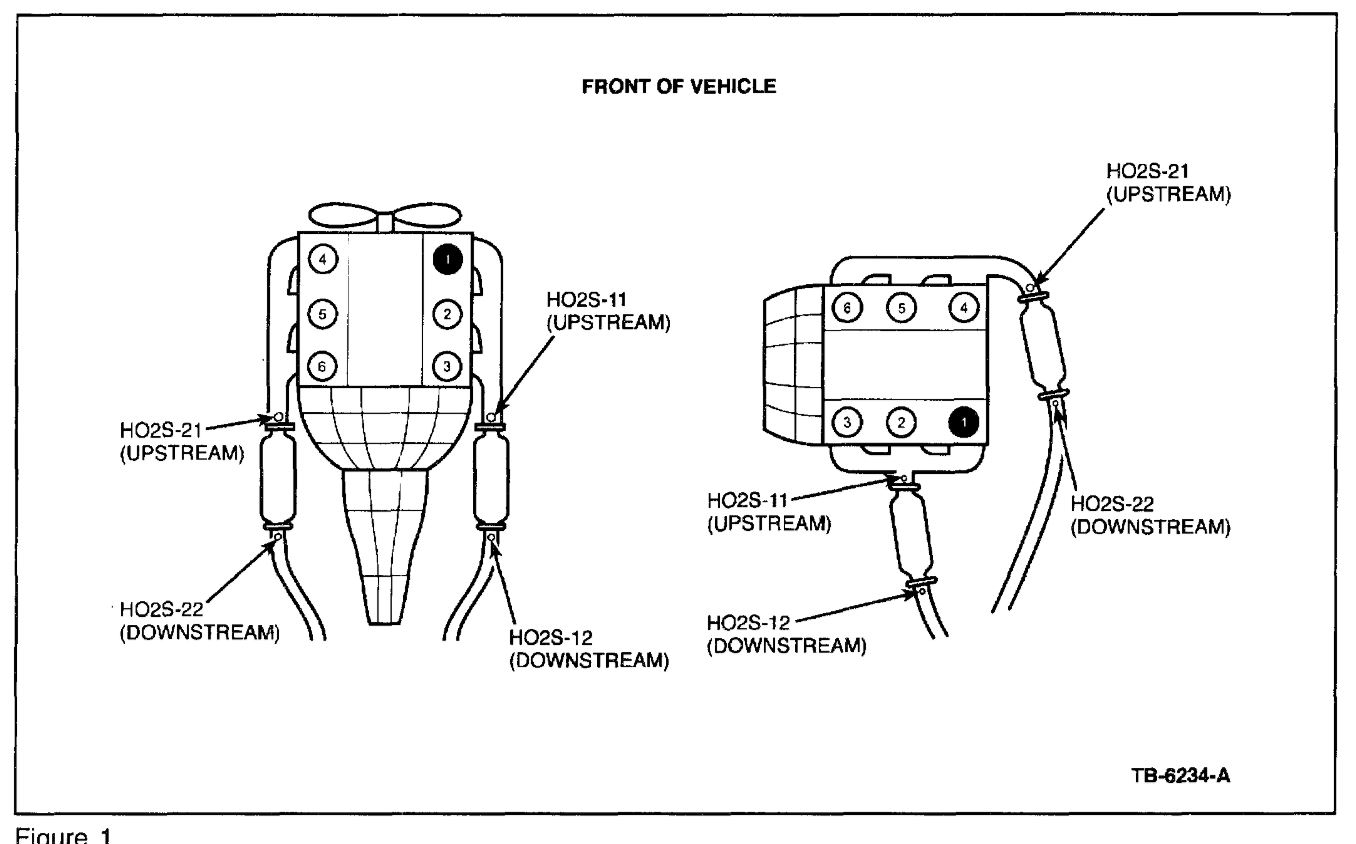
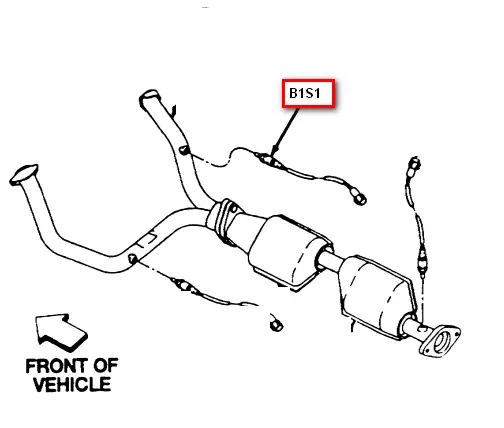
The 1999 Ford Explorer is equipped with two oxygen sensors – an upstream sensor (also known as the pre-catalytic converter sensor) and a downstream sensor (post-catalytic converter sensor).
Identifying the Bank and Sensor Position
To locate the oxygen sensors, you need to identify the bank and sensor positions. The bank refers to the side of the engine where the sensor is located, while the sensor position refers to whether it is located before or after the catalytic converter.
Tools and Equipment Needed for Sensor Location
To locate the oxygen sensor in a 1999 Ford Explorer, you will need the following tools and equipment:
- Jack stands or ramps for vehicle elevation
- Flashlight for better visibility
- Oxygen sensor socket or a suitable wrench for removal
- Penetrating oil to loosen any rusted connections
- Safety goggles and gloves for protection
Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the Oxygen Sensor
Preparing the Vehicle for Sensor Location
Start by ensuring that the vehicle is parked on a flat surface and the engine is turned off. Use the jack stands or ramps to elevate the front of the vehicle, providing enough clearance to access the oxygen sensors safely.
Locating the Upstream Oxygen Sensor
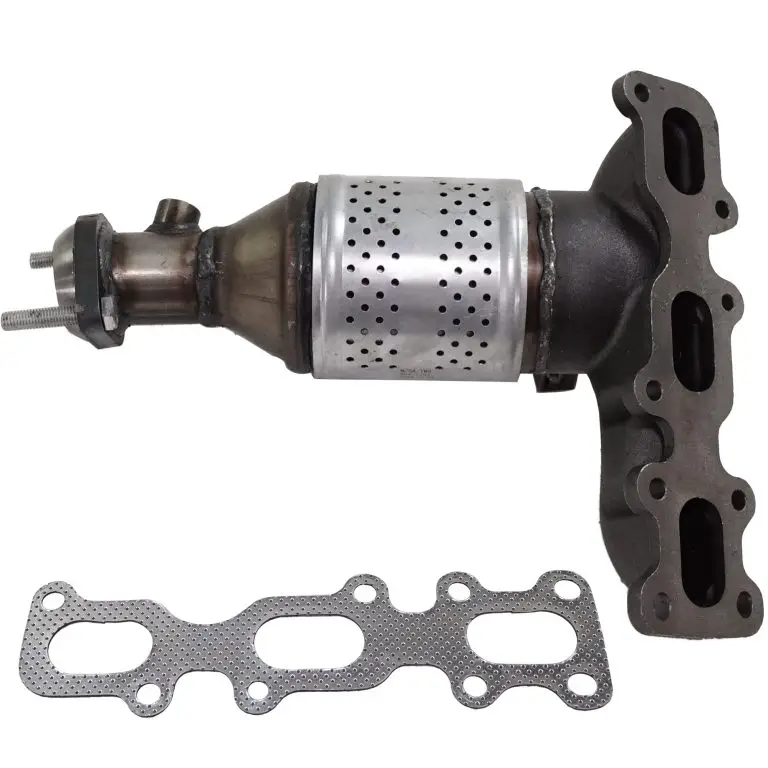
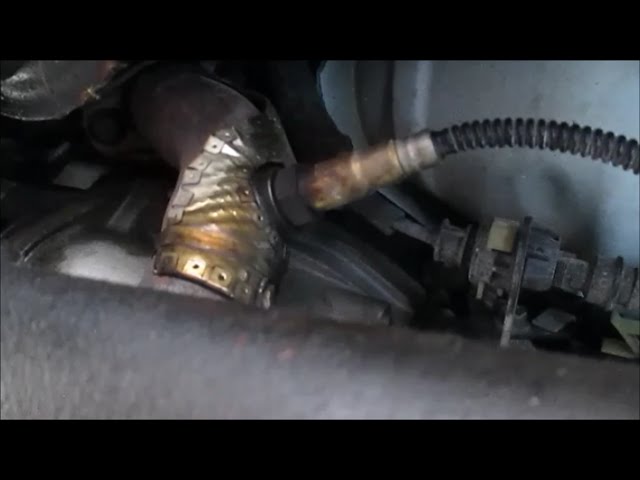
The upstream oxygen sensor is located before the catalytic converter. In the 1999 Ford Explorer, it is typically found on the exhaust manifold or the exhaust pipe near the engine. Use a flashlight to locate the sensor and identify any connectors or wiring attached to it.
Finding the Downstream Oxygen Sensor
The downstream oxygen sensor is located after the catalytic converter. In the 1999 Ford Explorer, it is usually positioned on the exhaust pipe downstream of the converter. Again, use a flashlight to locate the sensor and inspect the connectors or wiring.

Removing and Replacing the Oxygen Sensor
Safety Precautions
Before removing the oxygen sensor, it is crucial to take some safety precautions. Ensure that the vehicle is turned off, and the engine has cooled down to prevent burns. Wear safety goggles and gloves to protect yourself from any potential hazards.
Removing the Faulty Oxygen Sensor
To remove the faulty oxygen sensor, you will need an oxygen sensor socket or a suitable wrench. Disconnect any connectors or wiring attached to the sensor, and then use the socket or wrench to loosen and remove it from its position. Apply penetrating oil if the sensor is rusted or stuck.
Installing the New Oxygen Sensor
Before installing the new oxygen sensor, apply a small amount of anti-seize compound to the sensor threads to prevent corrosion and make future removal easier. Install the sensor by hand and then tighten it using the oxygen sensor socket or wrench. Reconnect any connectors or wiring.
Common Mistakes to Avoid when Replacing the Oxygen Sensor
Not Disconnecting the Battery
It is essential to disconnect the negative terminal of the vehicle’s battery before replacing the oxygen sensor. This helps prevent any electrical short circuits and protects the sensor and other sensitive components.
Using the Wrong Tools
Using the wrong tools, such as a regular socket instead of an oxygen sensor socket, can lead to damaging the sensor or other nearby components. Ensure you have the correct tools for the job to avoid any unnecessary complications.
Failure to Apply Anti-Seize Compound
Failing to apply anti-seize compound to the new oxygen sensor’s threads can cause the sensor to seize in the future, making it difficult to remove. Applying the compound ensures smooth removal and installation during future sensor replacements.
Testing the Oxygen Sensor
Using an OBD-II Scanner
To test the functionality of the oxygen sensor, you can use an OBD-II scanner. Connect the scanner to the OBD-II port of the vehicle and follow the instructions provided by the scanner to access the oxygen sensor readings. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the sensor is operating correctly.
Inspecting the Sensor’s Voltage
Another method to test the oxygen sensor is by inspecting its voltage output using a digital multimeter. Connect the multimeter to the oxygen sensor’s electrical connector and set it to the voltage measurement setting. Start the engine and observe the voltage readings. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the sensor is working correctly.
Performing an Oxygen Sensor Output Test
Some advanced diagnostic tools allow you to perform an oxygen sensor output test. These tests simulate different operating conditions and measure the sensor’s response. Follow the instructions provided by the diagnostic tool to perform the output test and interpret the results accordingly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How many oxygen sensors does a 1999 Ford Explorer have?
The 1999 Ford Explorer has two oxygen sensors – an upstream sensor and a downstream sensor.
Where can I purchase a replacement oxygen sensor for a 1999 Ford Explorer?
You can purchase a replacement oxygen sensor for a 1999 Ford Explorer from various sources, including auto parts stores, online retailers, or directly from Ford dealerships.
Can a faulty oxygen sensor cause other issues in my Ford Explorer?
Yes, a faulty oxygen sensor can cause various issues in your Ford Explorer, including decreased fuel efficiency, poor performance, and emissions problems.
Do I need to reset the computer after replacing the oxygen sensor?
In most cases, the vehicle’s ECU will automatically adjust to the new oxygen sensor readings. However, it is recommended to consult the vehicle’s owner’s manual or a mechanic to determine if a computer reset is necessary.
Can I drive my Ford Explorer with a faulty oxygen sensor?
While it is possible to drive with a faulty oxygen sensor, it is not recommended. A faulty sensor can negatively affect the vehicle’s fuel efficiency, performance, and emissions. It is best to have the sensor replaced as soon as possible.