High Pressure Oil Pump 7.3 Diesel Diagram & System Guide
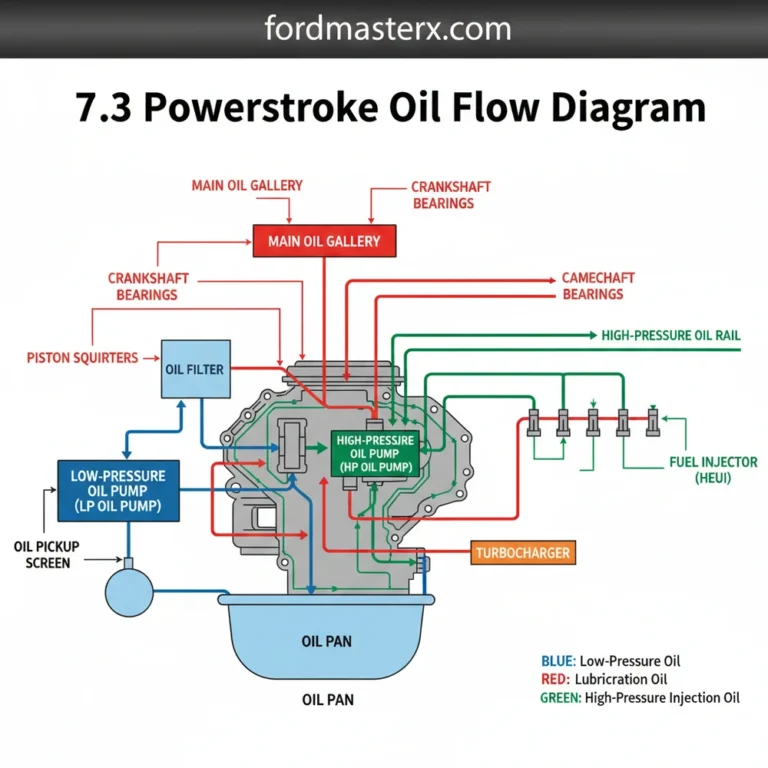
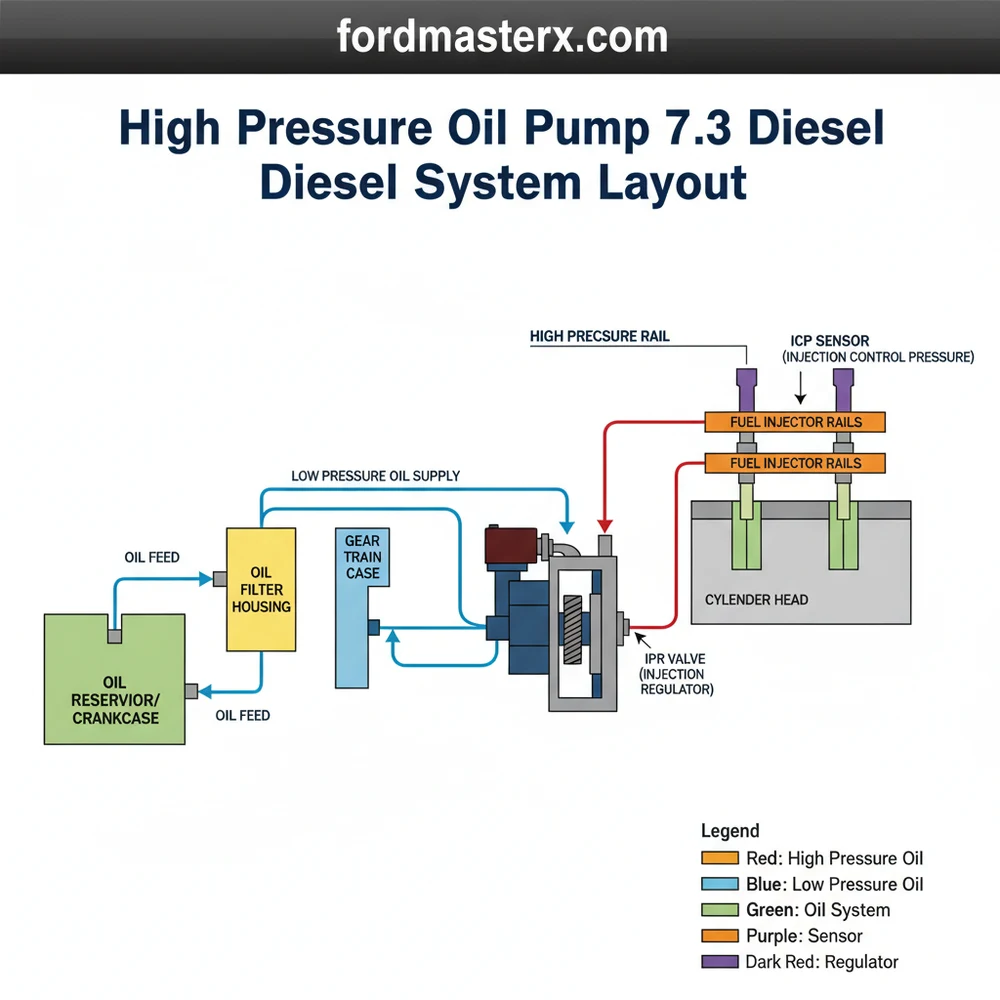
The high pressure oil pump 7.3 diesel diagram illustrates the hydraulic system layout responsible for powering HEUI injectors. It shows how oil flows from the reservoir through the HPOP and into the cylinder head rails, regulated by the IPR valve to ensure precise injection timing and pressure.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Identifies the HPOP as the heart of the HEUI fuel injection system
- Highlights the importance of the IPR valve for pressure regulation
- Shows the critical path of high-pressure lines to the cylinder heads
- Essential for diagnosing no-start or low-power issues in Powerstroke engines
- Use this diagram whenever performing maintenance on the high-pressure oil circuit
This comprehensive guide explains the high pressure oil pump 7.3 diesel diagram in detail. Understanding this diagram is essential for proper implementation and troubleshooting.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the High Pressure Oil Pump 7.3 Diesel Diagram & System Guide
Identify – Start with identifying the HPOP reservoir located at the top-front of the engine block.
Locate – Locate the Injection Pressure Regulator (IPR) valve attached to the back of the pump structure.
Understand – Understand how the high-pressure lines exit the pump and travel to the intake side of the heads.
Connect – Connect the diagnostic gauge or scanner to verify the actual HPOP pressure against the diagram specifications.
Verify – Verify that all O-rings and fittings in the system configuration are free of cracks or leaks.
Complete – Complete the inspection by ensuring the HPOP drive gear bolt is torqued to the manufacturer’s specific requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is the high pressure oil pump located?
The high pressure oil pump on a 7.3 Powerstroke is located in the engine valley, directly behind the front cover. It sits underneath the fuel filter housing and is driven by the engine’s gear train. You must remove the fuel bowl to access it clearly for service.
What does this HPOP diagram show?
The diagram illustrates the complete system layout, including the oil reservoir, the pump itself, the Injection Pressure Regulator (IPR) valve, and the high-pressure lines. It shows the flow configuration from the low-pressure pump into the HPOP and out to the left and right cylinder head oil rails.
How many connections does the HPOP have?
The HPOP typically features four primary connections: an oil inlet from the reservoir, two high-pressure discharge outlets (one for each cylinder head), and one mounting port for the IPR valve. Some aftermarket configurations may include a crossover line or an extra gauge port for monitoring oil pressure performance.
What are the symptoms of a bad HPOP?
Common symptoms include a hard start or no-start condition when the engine is hot, stalling at idle, or a significant loss of power under load. A failing pump or leaking O-rings in the system configuration will prevent the injectors from reaching the minimum 500 PSI required for firing.
Can I replace the 7.3 HPOP myself?
Yes, a DIY replacement is feasible for those with moderate mechanical experience. The process involves removing the fuel bowl and lines to reach the pump. While it is time-consuming, using a diagram helps ensure every component is reinstalled correctly and the high-pressure lines are sealed to prevent leaks.
What tools do I need for HPOP service?
You will need a standard socket set, a torque wrench, and a specialized IPR socket. Additionally, a fuel line disconnect tool and new O-rings for the high-pressure lines are essential. Always have a clean workspace and rags ready, as the HPOP reservoir contains a significant amount of oil.