F350 Fuse Box Diagram: Easy Identification Guide
The 2003 f350 fuse box diagram identifies two primary locations: the passenger compartment panel under the steering column and the power distribution box in the engine bay. These charts help locate fuses for the ECU and OBD-II port, which is essential when troubleshooting a check engine light or power loss.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Identifies the location and rating of every circuit in the vehicle
- Distinguishes between cabin fuses and high-current engine relays
- Crucial for restoring power to the diagnostic port and computer
- Always use the correct amperage to prevent electrical damage
- Essential first step before performing complex electrical repairs
Troubleshooting electrical gremlins in a heavy-duty truck can be a daunting task without a roadmap. if you are operating a Super Duty, having a reliable 2003 f350 fuse box diagram is the single most important tool in your arsenal. This guide provides a detailed breakdown of the power distribution centers, helping you pinpoint issues from dead power windows to critical engine management failures. Whether you are dealing with a sudden stall or a flickering instrument cluster, understanding how your electrical system is routed ensures your truck stays on the road and out of the shop. You will learn how to identify specific circuits, replace blown components safely, and use your fuse box to diagnose deeper mechanical issues.
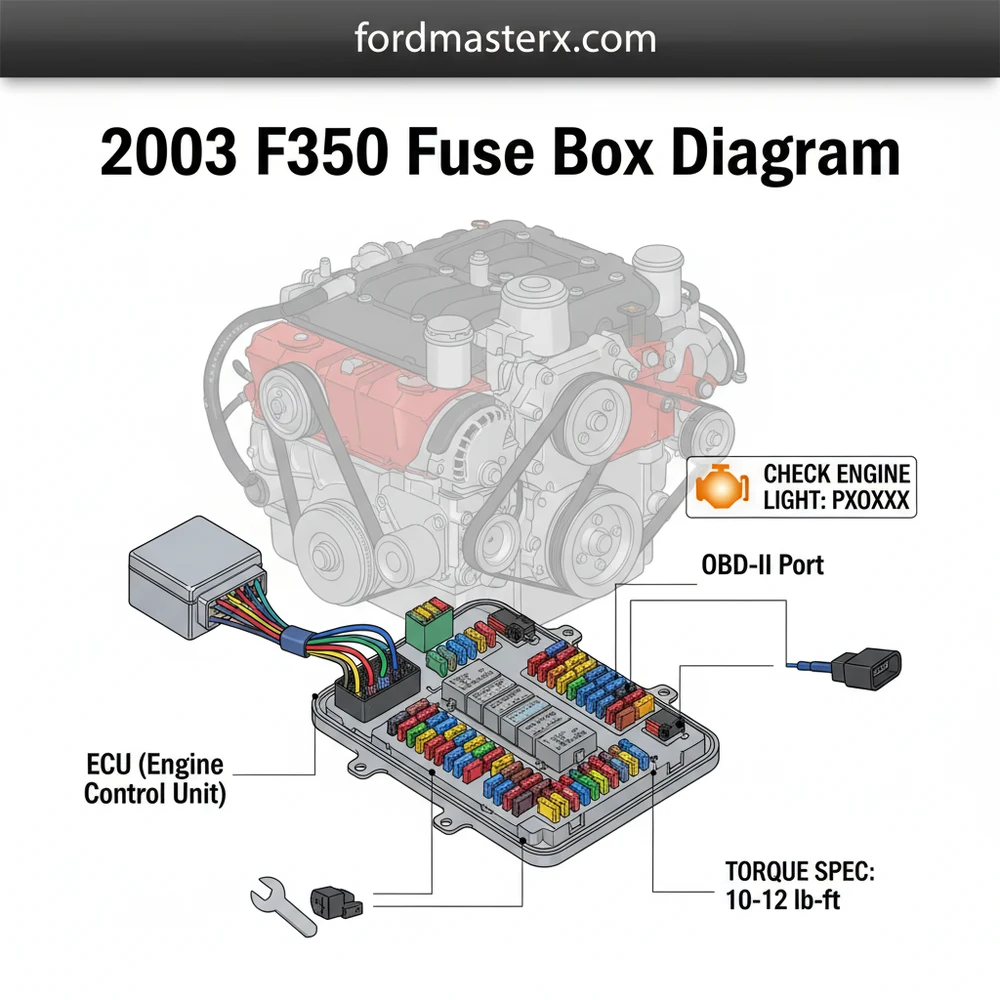
Understanding the 2003 F350 Fuse Box Layout
The 2003 Ford F-350 utilizes a dual-panel system to manage its extensive electrical demands. This configuration separates low-voltage interior electronics from high-current engine components. The primary 2003 f350 fuse box diagram identifies two distinct locations: the Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel and the Power Distribution Box located under the hood. The interior panel, tucked under the dashboard on the driver’s side, primarily manages cabin comforts, the ECU signal wires, and the lighting systems. In contrast, the engine bay box houses the heavy-duty “Maxi” fuses and relays that handle the starter motor, fuel pump, and trailer towing equipment.
Most electrical diagnostic issues on the 2003 model stem from Fuse 3 (20A) in the cabin panel, which powers the OBD-II diagnostic port and the cigar lighter. If your code reader won’t turn on, check this fuse first.
The diagram components are categorized by their amperage and function. Color-coding is a standard feature; for instance, tan fuses represent 5A, red represents 10A, blue is 15A, and yellow is 20A. High-current J-Case fuses in the engine bay are often larger and clear-topped to allow for easy visual inspection. Variations may exist between the 5.4L V8, 6.8L V10, and the 6.0L PowerStroke Diesel models. Specifically, the diesel variant includes additional relays for the glow plug control module and fuel heaters, which are not present in the gasoline versions. When reading the diagram, always verify if your specific truck has the “High-Line” trim package, as this includes additional fuses for heated seats and parking sensors.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the Fuse Box Diagram

Interpreting a complex wiring map requires a systematic approach. Follow these steps to diagnose and resolve electrical issues using your 2003 f350 fuse box diagram:
- 1. Locate the Access Points: The interior panel is located beneath the steering column. You will need to turn the plastic fasteners to remove the cover. The engine compartment box is located on the driver-side fender well, housed in a black plastic rectangular box with a snap-on lid.
- 2. Orient the Diagram: Compare the physical layout of the fuses to the printed diagram on the inside of the cover. Look for the “keyway” or a notched corner on the box to ensure you aren’t reading the diagram upside down.
- 3. Identify the Faulty Circuit: If your check engine light is illuminated, start by checking the power to the ECU. If you are experiencing cooling issues, look for the fuse controlling the coolant flow sensors or the electronic fan clutch relay.
- 4. Inspect the Fuse: Use a plastic fuse puller tool (usually found inside the fuse box cover) to remove the suspected fuse. Hold it up to a light source. If the metal bridge inside the plastic housing is broken or if there is a dark burn mark, the fuse is blown.
- 5. Cross-Reference Amperage: Never replace a blown fuse with one of a higher amperage. If the diagram calls for a 15A blue fuse, only use a 15A replacement. Using a higher rating can lead to melted wires or a vehicle fire.
- 6. Test for Continuity: For relays or larger Maxi-fuses, a visual check might not be enough. Use a multimeter set to the “Ohms” or “Continuity” setting. Touch the probes to the two metal tabs on the top of the fuse. A “beep” indicates a healthy circuit.
Always turn off the ignition and disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on high-current fuses in the engine bay. This prevents accidental short circuits that could damage the sensitive ECU.
When reinstalling the battery cables after your work, ensure you follow the proper torque spec for the terminal clamps. Loose battery connections can mimic blown fuses by causing intermittent power loss or preventing the alternator from charging the system properly. While you are under the hood, it is also wise to perform a visual check of the accessory belt. A slipping belt can result in low voltage, which may trigger phantom fuse-related codes in the diagnostic system.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting

Many 2003 F-350 owners encounter specific electrical patterns. One of the most frequent issues is a lack of communication with the OBD-II scanner. When a technician cannot pull a diagnostic code, it is almost always due to a blown fuse in the cabin panel that shares a circuit with the cigarette lighter. Another common problem involves the trailer tow lights; if the truck’s blinkers work but the trailer’s do not, the dedicated “Tow” fuses in the engine compartment distribution box are the likely culprits.
If you notice your check engine light flickering or the engine stalling unexpectedly, it may not be a mechanical failure of the timing chain or fuel injectors. Instead, inspect the PCM (Powertrain Control Module) relay. These relays can become heat-soaked over time, leading to intermittent contact. If the truck cranks but won’t start, listen for the fuel pump. If it’s silent, the fuel pump relay in the engine bay box is the first place to look before assuming the pump itself has failed. Seeking professional help is recommended if you replace a fuse and it immediately blows again, as this indicates a direct “short to ground” in the wiring harness.
Tips and Best Practices for Electrical Maintenance
Maintaining the integrity of your F-350’s electrical system goes beyond just swapping fuses. To ensure long-term reliability, follow these professional recommendations:
- ✓ Keep it Dry: Ensure the gaskets on the under-hood power distribution box are intact. Moisture entry is a primary cause of corrosion on relay pins, which can lead to overheating and circuit failure.
- ✓ Use Quality Components: Avoid “bulk” unbranded fuses from discount bins. High-quality, name-brand fuses are manufactured to more precise tolerances and are less likely to cause damage to your expensive ECU.
- ✓ Dielectric Grease: When replacing relays, a small amount of dielectric grease on the prongs can prevent oxidation, especially if you live in a salt-belt state or use your truck for snow plowing.
Always keep a spare kit containing 10A, 15A, and 20A mini-fuses, along with a spare 30A Maxi-fuse, in your glovebox. Most roadside electrical failures can be solved in minutes if you have the parts on hand.
Finally, remember that the electrical system is connected to the mechanical health of the vehicle. For instance, an overworked alternator caused by a glazed accessory belt can create voltage spikes that weaken fuses over time. Similarly, issues with coolant flow sensors can sometimes be traced back to corroded fuse terminals rather than a faulty sensor. By using a 2003 f350 fuse box diagram as a preventive maintenance map, you can identify these small issues before they become expensive repairs. Regular inspection of the fuse panels should be part of your seasonal maintenance routine, alongside checking fluid levels and tire pressures.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is the fuse box located?
The 2003 f350 fuse box diagram shows two locations. The interior panel is positioned under the dashboard to the left of the steering column. The secondary power distribution box is located under the hood on the driver’s side, containing high-amperage fuses and relays for engine components and towing.
What does the fuse box diagram show?
This diagram provides a visual map of all electrical protection devices, including fuses, diodes, and relays. It lists the numerical position, the amperage rating, and the specific equipment each fuse controls, such as the radio, headlights, ECU, or the cigarette lighter, which often powers the diagnostic port.
How many pins do the relays have?
Most relays in the F350 system use a standard four or five-pin configuration. The 2003 f350 fuse box diagram identifies which relay controls high-draw systems. If a relay fails, it may trigger a diagnostic code, so ensuring the pins are seated correctly in the socket is vital for operation.
What are the symptoms of a bad fuse?
A bad fuse typically results in a sudden loss of power to a specific component, such as the check engine light failing to illuminate or the OBD-II port not communicating. You may see a broken metal filament inside the clear plastic fuse housing or experience intermittent electrical system failures.
Can I replace the fuses myself?
Yes, replacing a fuse is a straightforward DIY task. Use the 2003 f350 fuse box diagram to find the correct location, pull the old fuse, and insert a new one of the same color and amperage. It is an easy way to resolve issues before seeking professional mechanical help.
What tools do I need for this task?
You only need a plastic fuse puller tool and a basic multimeter to test for continuity. If you are removing the entire battery junction box, you might need a socket set. When reinstalling mounting bolts, always check the service manual for the correct torque spec to avoid damaging the plastic.






