5.4 Triton Ford 5.4 Firing Order Diagram: Complete Guide
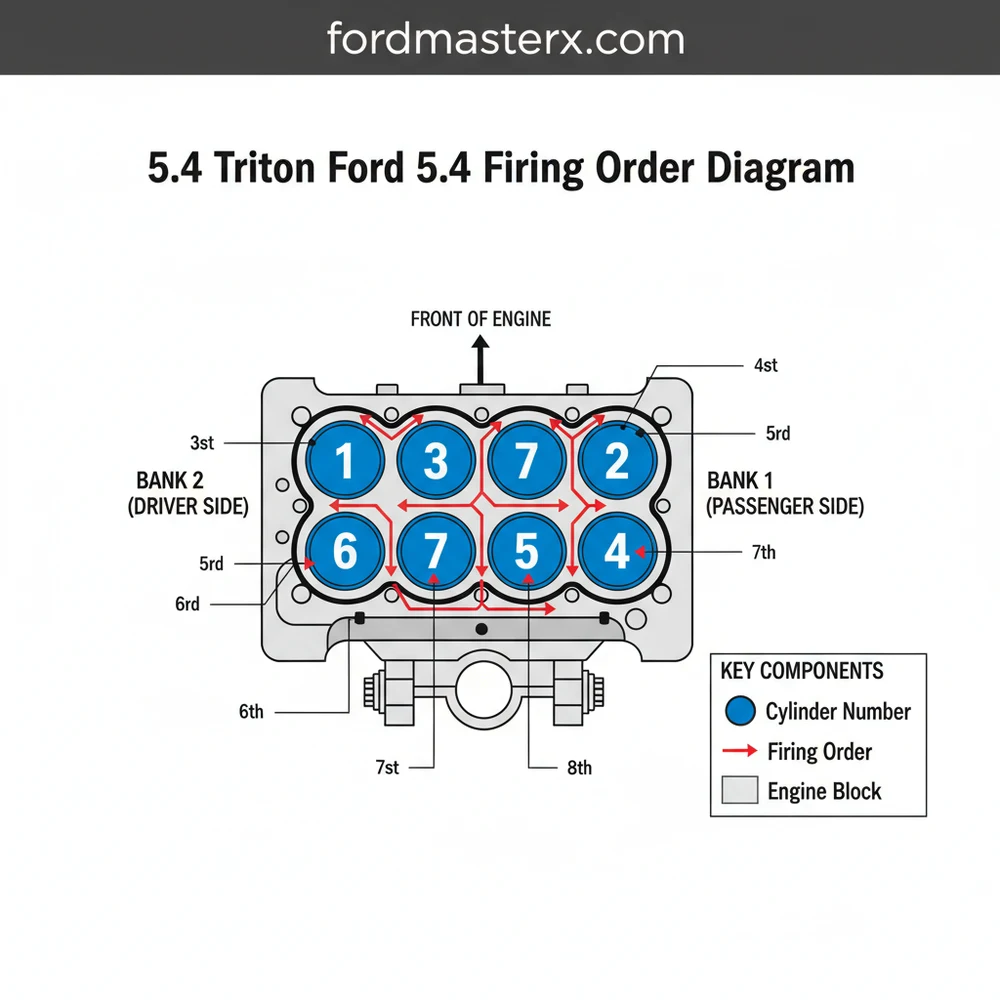
The firing order for the Ford 5.4 Triton V8 engine is 1-3-7-2-6-5-4-8. Cylinders are numbered 1-4 on the passenger side and 5-8 on the driver side. This specific configuration is essential for correct ignition timing, ensuring the engine structure remains balanced and runs smoothly without mechanical interference.
📌 Key Takeaways
- The primary purpose is to identify the 1-3-7-2-6-5-4-8 ignition sequence
- Correctly identify cylinder 1 at the front of the passenger side bank
- Ensure all Coil-on-Plug connections are secure to prevent misfires
- Use this diagram when diagnosing P0300-P0308 engine codes
- Always verify the layout before replacing spark plugs or coils
When performing maintenance or repairs on one of the most widely used V8 engines in automotive history, having access to an accurate 5.4 triton ford 5.4 firing order diagram is essential for ensuring peak performance and engine longevity. Whether you are dealing with a rough idle, a persistent misfire, or are simply replacing spark plugs and ignition coils, understanding the specific sequence in which the cylinders fire is the foundation of a successful job. This guide provides a detailed overview of the engine’s cylinder layout and firing configuration, helping you navigate the complexities of the Triton V8 system with confidence and technical precision. By the end of this article, you will be able to identify every ignition component and troubleshoot common timing-related issues effectively.
The Ford 5.4L Triton V8 engine uses a specific cylinder numbering system: the passenger side bank is numbered 1-4 (front to back) and the driver side bank is numbered 5-8 (front to back). The firing order is 1-3-7-2-6-5-4-8.
The 5.4 Triton V8 engine utilizes a specific internal architecture that dictates how the ignition system interacts with the mechanical components. In this schematic, the engine is viewed from the front (the radiator side), which is the standard perspective for most automotive blueprints. The 5.4 Triton follows Ford’s traditional cylinder numbering system, which differs from some other manufacturers like GM or Chrysler. On the passenger side (the right side if you are sitting in the driver’s seat), the cylinders are numbered 1, 2, 3, and 4, starting from the front of the vehicle and moving toward the firewall. On the driver’s side (left side), the cylinders are numbered 5, 6, 7, and 8, again starting from the front and moving back. This linear layout is a core part of the engine’s structure and is vital for identifying which coil-on-plug (COP) unit corresponds to specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
The firing order for this engine is 1-3-7-2-6-5-4-8. This sequence is designed to balance the rotational forces on the crankshaft and provide smooth power delivery. In the diagram, the ignition sequence starts at the front passenger side (Cylinder 1), jumps to the third cylinder on that same bank, then crosses over to the rear of the driver’s side (Cylinder 7), and continues through the established configuration. Understanding this blueprint is the first step in diagnosing ignition timing issues or routing replacement wiring harnesses correctly.
Interpreting the 5.4 triton ford 5.4 firing order diagram and applying it to your vehicle requires a methodical approach. Follow these steps to ensure you are identifying the components correctly and maintaining the integrity of the ignition system.
- 1. Identify the Front of the Engine: Begin by standing at the front bumper looking toward the windshield. The front of the engine is defined by the location of the accessory drive belts, alternator, and cooling fan. This is your “Point Zero” for reading any engine schematic.
- 2. Locate Cylinder Number One: According to the Ford configuration, Cylinder 1 is always the forward-most cylinder on the passenger side (right side when facing the engine). Knowing this location is critical because the entire firing sequence is timed based on the position of this specific piston during its compression stroke.
- 3. Map the Cylinder Banks: Visualize the engine in two banks. The passenger side bank contains cylinders 1, 2, 3, and 4. The driver side bank contains 5, 6, 7, and 8. If you receive a “Cylinder 5 Misfire” code (P0305) from an OBD-II scanner, you will immediately know to look at the front-most cylinder on the driver’s side.
- 4. Understand the Coil-on-Plug (COP) System: Most 5.4 Triton engines use a COP system where each cylinder has its own dedicated ignition coil sitting directly on top of the spark plug. Unlike older engines with a distributor and long spark plug wires, the layout here consists of individual electrical connectors.
- 5. Verify the Firing Sequence: Using the firing order 1-3-7-2-6-5-4-8, you can understand how the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) cycles the spark. This is vital if you are diagnosing a complex issue like a wiring harness fault that might be affecting multiple cylinders in the sequence.
- 6. Prepare Necessary Tools: You will typically need a 7mm or 8mm socket for the coil hold-down bolts, a 5/8″ or 9/16″ spark plug socket (depending on the specific Triton head design), and a variety of extensions to reach the cylinders near the firewall.
- 7. Inspect the Ignition Harness: While following the diagram, check the plastic connectors at each coil. These are notorious for becoming brittle due to engine heat. Ensure they click into place securely and that the pins are not corroded.
- 8. Apply Dielectric Grease: When reinstalling coils based on the diagram, apply a small amount of dielectric grease to the inside of the rubber boot. This prevents moisture intrusion and ensures a solid electrical path to the spark plug.
Always ensure the engine is completely cool before working on the ignition system. The 5.4 Triton engine is known for specific spark plug challenges, including carbon buildup that can cause plugs to seize. Rushing the removal process can lead to damaged threads in the aluminum cylinder heads, necessitating expensive repairs.
The most common issue owners face is a “dead miss” or a “stumble” under load, often caused by a failing ignition coil or a fouled spark plug. By using the 5.4 triton ford 5.4 firing order diagram, you can pinpoint exactly which cylinder is misbehaving when a scanner provides a code like P0301 through P0308. For instance, a P0307 code indicates a problem with the second cylinder from the back on the driver’s side.
Another frequent problem is moisture accumulation in the spark plug wells, especially in cylinders 4 and 8, which are those closest to the firewall. If the diagram shows a fault in these rear cylinders, check for leaking heater hoses or cowl drainage issues that might be dripping water onto the coils. If you notice a “Check Engine” light flashing, this indicates a catalyst-damaging misfire. In such cases, use the schematic to identify and replace the faulty component immediately. If the misfire persists after replacing the coil and plug, it may be time to seek professional help to test for fuel injector failure or mechanical compression loss within that specific cylinder structure.
To keep your Triton engine running smoothly, always prioritize high-quality components. When replacing parts identified via the 5.4 triton ford 5.4 firing order diagram, it is highly recommended to use Motorcraft ignition coils and spark plugs. The Triton’s ignition system is exceptionally sensitive to resistance variances; aftermarket “bargain” coils often fail prematurely or cause intermittent radio interference that can confuse the vehicle’s electronic system.
When removing spark plugs from a 3-valve 5.4 engine, use a dedicated spark plug cleaner or compressed air to blow out any debris from the well before removal. This prevents dirt from falling into the combustion chamber, which can cause internal damage.
Another best practice is to label your ignition wires or coil connectors if you are removing multiple units at once for a deep clean or manifold repair. Even though the harness is usually length-specific, labeling them according to the cylinder numbers (1-8) prevents any accidental cross-connection. Regularly inspecting the rubber boots on your coils for cracks can save you from a breakdown; even a tiny hairline fracture can allow the high-voltage spark to “arc” to the cylinder head rather than reaching the plug. This results in a misfire that follows the rhythmic pulse of the firing order. By maintaining this system and following the correct configuration, you ensure your Ford 5.4 Triton remains a reliable powerhouse for years to come.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the 5.4 Triton Ford 5.4 Firing Order Diagram: Complete Guide
Identify the passenger and driver side cylinder banks on the engine.
Locate cylinder one at the front-most position on the passenger side.
Understand how the 1-3-7-2-6-5-4-8 sequence maps to the physical layout.
Connect each ignition coil according to the specific cylinder numbering.
Verify that every connector in the system is fully seated and locked.
Complete the task by starting the engine to confirm smooth ignition timing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is the number 1 cylinder located?
Cylinder 1 on the 5.4 Triton is located at the front of the engine on the passenger side. This starting point is essential for following the firing order configuration and correctly identifying which component needs service during a routine repair or complex engine diagnosis.
What does this firing order diagram show?
The diagram illustrates the specific sequence in which each cylinder ignites and the physical layout of the cylinders on the engine block. It shows how the ignition system distributes power across the V8 structure, helping you visualize the cylinder numbering for accurate maintenance.
How many ignition coils does the 5.4 Triton have?
The 5.4 Triton V8 engine utilizes eight individual ignition coils in a Coil-on-Plug (COP) system. This configuration allows for precise spark timing based on the firing order, which improves overall fuel efficiency and reduces the risk of a complete system failure during operation.
What are the symptoms of a bad ignition coil?
Symptoms of a failing ignition component include engine hesitation, rough idling, a significant drop in fuel economy, and a ‘Check Engine’ light. These issues typically stem from a disruption in the firing order layout, preventing one or more cylinders from contributing to the engine’s power.
Can I replace the spark plugs myself?
Yes, you can replace the spark plugs, but the deep cylinder structure of the Triton engine makes it a delicate task. By following the firing order diagram, you can work systematically through the layout, ensuring each plug is properly gapped and installed without damaging the threads.
What tools do I need for ignition service?
To service the ignition system, you will need a 7mm socket for the coil bolts and a specialized 9/16-inch spark plug socket. These tools allow you to access the deep-set configuration of the 5.4 Triton engine for successful spark plug or coil replacement.







