Best Power Inverter For Truck: Top Curated Models For Reliability And Performance
For professional drivers and overlanders, a truck is more than a vehicle; it is a mobile office, kitchen, and living space that demands reliable AC power. Relying on the standard DC outlets for heavy-duty needs is a recipe for frustration. Cheap, under-powered inverters frequently fail under the stress of daily use or, worse, damage sensitive equipment like laptops and medical devices due to poor signal quality. This guide will identify the best power inverters for trucks on the market today, breaking down the technical specifications and installation requirements essential for high-performance mobile power. By understanding the intersection of amperage, signal fidelity, and thermal management, you can ensure your cabin remains powered safely and efficiently through any haul.
Pure Sine Wave vs. Modified Sine Wave: Essential Technical Distinctions

📤 Share Image
When selecting from a curated list of power inverters, the most critical decision involves the internal architecture of the power conversion. The distinction between Pure Sine Wave (PSW) and Modified Sine Wave (MSW) is not merely academic; it dictates whether your sensitive electronics will thrive or fail. A Pure Sine Wave inverter replicates the smooth, oscillating power provided by the utility grid. In contrast, Modified Sine Wave units produce a “blocky,” stepped approximation of a wave.
The primary metric here is Total Harmonic Distortion (THD). High-quality PSW inverters typically maintain THD below 3%, whereas modified units can reach a staggering 40% THD. This distortion introduces “electrical noise” into the system, which can be catastrophic for microprocessor-controlled devices. For instance, a driver attempting to run a Keurig coffee maker on a modified sine wave inverter will frequently encounter ‘brewing errors’ or a complete pump failure, while the same machine operates flawlessly on a PSW unit. Beyond immediate errors, the high THD of MSW units can reduce the operational lifespan of high-end electronics by up to 30% due to heat buildup in the circuitry.
By The Numbers: Signal Quality
THD in Pure Sine Wave
THD in Modified Sine Wave
Furthermore, modified sine waves pose a mechanical risk to induction motors and cooling fans found in modern truck cabin appliances like refrigerators and CPAP machines. These motors are designed for a smooth signal; a stepped wave causes them to run hotter and less efficiently, often resulting in an audible “buzzing” sound and eventual motor burnout. While MSW inverters are cheaper, the cost-benefit analysis favors the PSW for long-haul durability. The initial savings of an MSW unit are quickly negated if you must replace a $1,000 laptop or a $500 CPAP machine prematurely.

Ranked Performance: The Best Power Inverters for Heavy-Duty Trucks
To help you navigate the selection of hardware available, we have ranked the top models based on real-world performance, surge capacity, and build quality. These units represent the recommended standards for different use cases in the trucking industry.
The 3000W Heavy-Duty Leader: Victron Energy MultiPlus
The Victron Energy MultiPlus is widely considered the gold standard for full sleeper-cab power requirements. It is a sophisticated inverter/charger capable of handling large microwaves, refrigerators, and power tools simultaneously. One of its standout features is the integration with smartphone apps via Bluetooth for real-time load monitoring. This allows drivers to see exactly how many amps are being drawn from the battery bank without leaving the driver’s seat. It also features ‘Soft Start’ technology, which manages high-inrush current demands—essential for starting the compressor on a portable fridge without tripping the breaker.
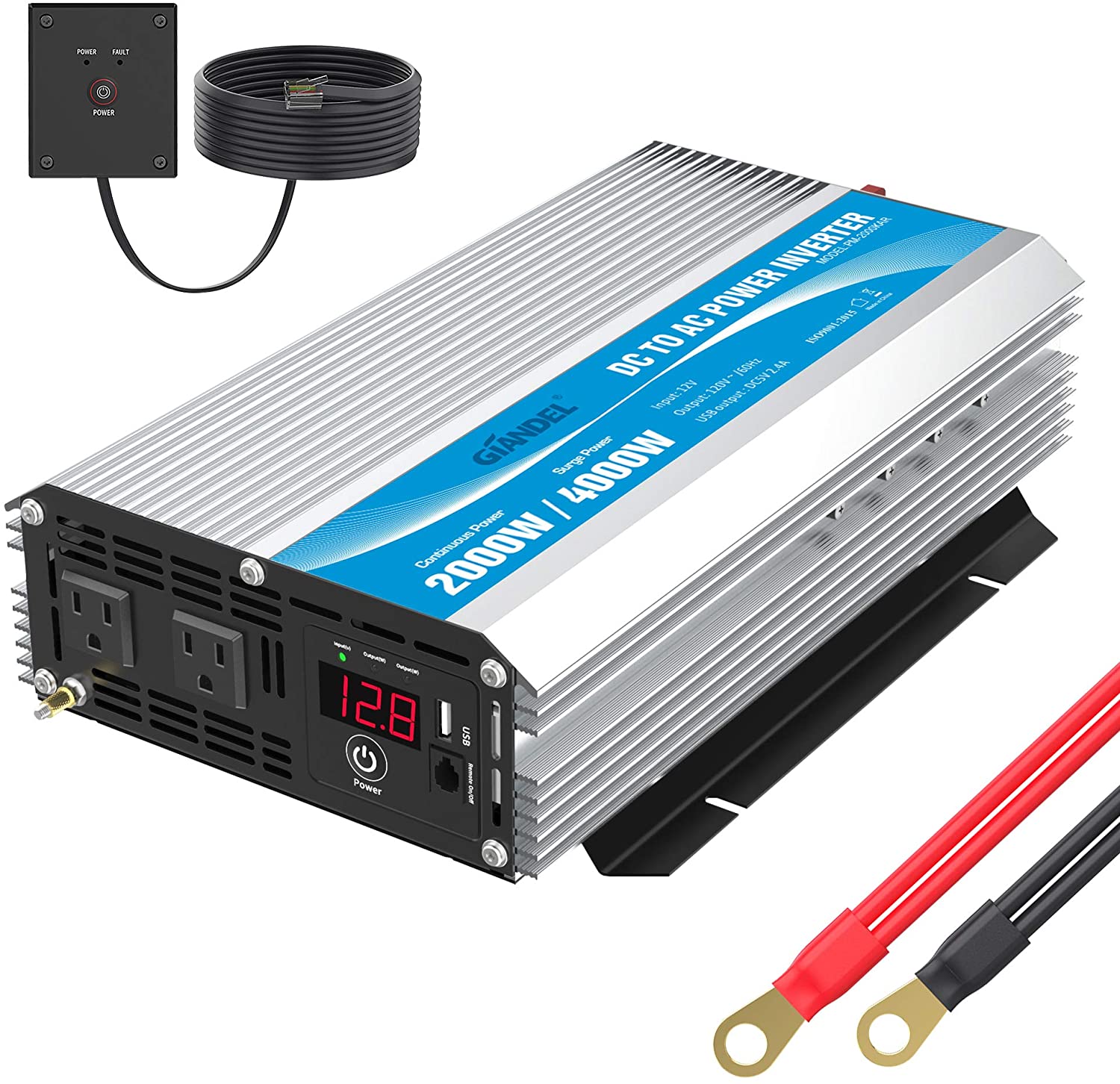
The 2000W Mid-Range Standard: Renogy Pure Sine Wave Inverter
For most drivers, a 2000W unit provides the ideal balance of footprint and capacity. The Renogy 2000W is a popular choice due to its high peak surge capacity, which can handle up to 4000W (200% of its continuous rating) for up to 1 second. This is vital for overcoming the initial resistance of motorized appliances. Its design includes thermal-controlled cooling fans that only activate when necessary, maintaining a quiet cabin environment while ensuring the unit never reaches critical operating temperatures.
The 1500W Reliable Choice: Cobra PRO 1500W
The Cobra PRO 1500W is a must-know model for drivers who value integrated convenience. It features fast-charge USB ports (USB-A and USB-C) built directly into the faceplate and supports a remote control panel for dashboard operation. It is robustly designed with GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) protected outlets, providing an essential layer of safety in mobile environments where vibrations could potentially loosen internal wiring over time.

Essential Installation Protocols for High-Wattage Inverter Systems
Even the highest-quality inverter will perform poorly—or become a fire hazard—if the installation is flawed. For high-wattage systems, cabling and fusing are not areas where you can afford to cut corners. A common error is using undersized wire, which leads to excessive voltage drop. Industry standards dictate that a 3% voltage drop is the maximum allowable for power-critical DC circuits; exceeding this can cause the inverter to shut down prematurely as it detects “low battery” voltage that isn’t actually there.
📋
Installation Checklist
Use 0-gauge copper cable for 3000W systems. Never use aluminum; its higher resistance generates dangerous heat under load compared to high-strand copper.
Place an ANL or Class T fuse within 7 inches of the battery terminal. This protects the truck’s entire electrical system if the main power cable shorts to the chassis.
Ensure the inverter’s ground lug is connected to the truck frame. This is required for the internal GFCI and safety features to function correctly during a fault.
Mounting is equally important. Inverters generate significant heat during the DC-to-AC conversion process. Avoid installing the unit in small, sealed compartments or near volatile gases (such as directly above lead-acid batteries). Consider a case study of two systems: One using 0-gauge copper cable remains cool to the touch at full load, while a system using 4-gauge aluminum cable in a 3000W setup will experience thermal runaway, potentially melting the insulation and causing a fire. Always prioritize airflow and oversized conductors for safety.
Must-Know Battery Management and Alternator Capacity Calculations
A common misconception is that the truck’s alternator can provide unlimited power while the engine is running. In reality, most standard truck alternators only provide 25-30% of their rated output at idle. If you are drawing 2000W (approximately 160-180 Amps at 12V), your alternator may not be able to keep up, leading to a net drain on your batteries even while idling. This is a critical factor for the longevity of the OEM alternator, as running it at its limit for extended periods causes premature diode failure.
A 1000W microwave draw is actually around 83-90 Amps from your 12V system when efficiency losses are considered. If you use a standard Group 31 battery, you should only run such high loads for a few minutes to avoid dropping below the 12.2V threshold required for engine cranking.
To manage this, professional installations often include Low Voltage Disconnect (LVD) settings. An LVD ensures the inverter shuts off before the battery bank is too depleted to start the engine. For drivers requiring extended stationary power, exploring secondary battery banks—specifically Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4)—is a superior alternative to standard AGM. Lithium batteries can be discharged to 90% without damage, whereas traditional lead-acid batteries should not be discharged below 50% for maximum lifespan.
Popular Smart Features: Remote Monitoring and Modern Interfaces
The evolution of inverter technology has brought about a collection of smart features that make life on the road significantly easier. Modern interfaces have moved beyond simple “on/off” switches to comprehensive energy management systems. High-end units now feature USB-C Power Delivery (PD) integration. This allows you to charge modern laptops at 60W or 100W directly from the DC-AC converter’s logic board, bypassing the need to use a bulky AC power brick and improving overall efficiency.
Eco-Mode Efficiency
High-end inverters have a ‘no-load’ current draw of less than 0.5 Amps in Eco-mode. Cheaper units can drain up to 2.0 Amps just by being idle, potentially killing your batteries overnight.
Remote Management
Bluetooth-enabled systems like Victron VE.Smart Networking allow you to monitor voltage and power consumption from your phone, providing a cleaner dashboard without extra wiring.
Digital LCD displays are no longer a luxury; they are essential. Real-time tracking of input voltage and output wattage allows you to diagnose issues before they cause a shutdown. For instance, if you see the input voltage dropping to 11.5V while the engine is running, you know your alternator is being overtaxed or your cabling has a loose connection. This transparency is what separates professional-grade equipment from budget consumer electronics.
Never bypass the inverter’s internal protections. If a unit repeatedly shuts down due to an “Overload” error, do not attempt to force it to run by using a larger fuse. This indicates your equipment is drawing more than the rated continuous wattage, which will eventually lead to internal component failure or fire.
In summary, the transition to high-fidelity Pure Sine Wave technology is the most impactful upgrade you can make for your truck’s cabin. By comparing ranked models like the Victron MultiPlus and Renogy 2000W, you can find a unit that matches your specific lifestyle needs—whether that’s powering a high-end gaming laptop or a full-sized microwave. Remember that the inverter is only one part of the system; proper cabling, 7-inch fusing protocols, and a clear understanding of your alternator’s idle capacity are the pillars of a safe and reliable installation. Audit your power requirements today and select an inverter that offers at least 20% more continuous wattage than your highest calculated load to ensure longevity and peak performance for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I run a microwave in my truck with a 1500W inverter?
While some 700W microwaves might run on a 1500W inverter, the ‘1500W’ rating of a microwave refers to the cooking power, not the electrical draw. Most microwaves require 1200W-1800W of electrical input. For consistent reliability and to handle the initial surge, a 2000W pure sine wave inverter is the recommended minimum for microwave use.
Will an inverter drain my truck battery if it is turned off?
Most modern inverters have a very small ‘parasitic draw’ even when switched off. However, if left in the ‘standby’ or ‘on’ position without a load, they can pull 0.5 to 2.0 Amps. For long-term storage, it is essential to use a physical battery disconnect switch or ensures the inverter is fully powered down to prevent battery depletion.
Is a modified sine wave inverter safe for my laptop?
Technically, most laptop power bricks can convert a modified sine wave, but it causes them to run significantly hotter and less efficiently. Over time, this heat can degrade the internal components of the laptop’s power supply. To protect expensive electronics, an essential best practice is to always use a pure sine wave inverter for microprocessor-based gear.
What gauge wire do I need for a 3000W inverter?
For a 3000W inverter on a 12V system, you are looking at over 250 Amps of current. You must use 0/0 (2/0) gauge high-strand copper cable for runs up to 10 feet. Using undersized wire will cause a significant voltage drop, potentially leading to the wire insulation melting and causing a fire.
Do I need to keep the truck engine running while using the inverter?
For low-wattage tasks like charging a phone, the engine can remain off. For high-draw appliances like heaters or microwaves, it is popular practice to keep the engine running. This allows the alternator to provide the necessary current and prevents the battery voltage from dropping below the inverter’s cutoff threshold.